MOS Tube H Bridge Motor Drive Circuit Diagram

H bridge is a typical DC motor control circuit, because its circuit shape resembles the letter H, so it is named "H bridge". Four audions constitute the four vertical legs of H, and the motor is the horizontal bar in H (note: the figure is only a schematic diagram, rather than a complete circuit diagram, in which the driving circuit of the audion is not drawn).
H bridge drive principle
1. Motor drive
Circuit first, single chip microcomputer can output dc signal, but its driving ability is limited, so MCU common drive signal, drive of power tube of the MOS tube, to produce a large current to drive motor, and size of duty ratio can pass drive chip control on the uniform voltage on the motor to reach the purpose of speed control. Motor drive mainly USES N channel MOSFET to build an H bridge drive circuit, H bridge is a typical DC motor control circuit, because its circuit shape resembles the letter H, so it is called an "H bridge". The four switches form the four vertical legs of H, and the motor is the horizontal bar in H. To make the motor run, a pair of switches on the diagonal must be switched on to control the positive and negative rotation of the motor through different current directions. Its connected circuit is shown in the figure.
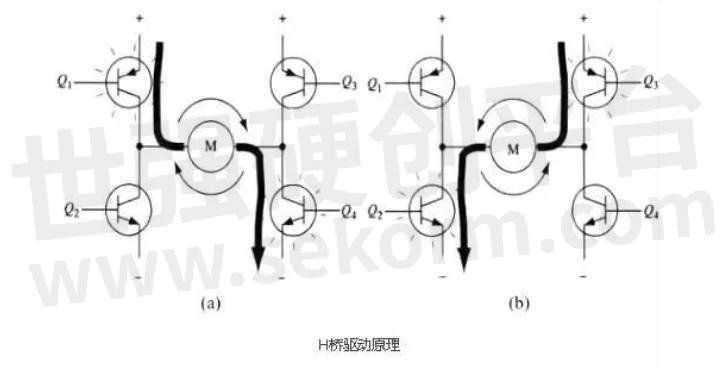
Fig.1
2. Driving principle of H bridge
In practice drive circuit usually uses a hardware circuit local control switch, motor drive board mainly USES two kinds of driver chips, one is full bridge drive HIP4082, one is half bridge drive IR2104, and the half bridge circuit is composed of two MOS transistor oscillation, the whole bridge circuit is composed of four MOS oscillator. Among them, the IR2104 half-bridge driver chip can drive high-end and low-end TWO N-channel MOSFET, can provide a larger grid drive current, and has hardware dead zone, hardware anti-on-arm conduction, and other functions. Two IR2104 type half-bridge driver chips can be used to form a complete DC motor H bridge drive circuit, and IR2104 low cost, function, output power relative to HIP4082 low, this plan adopts more.
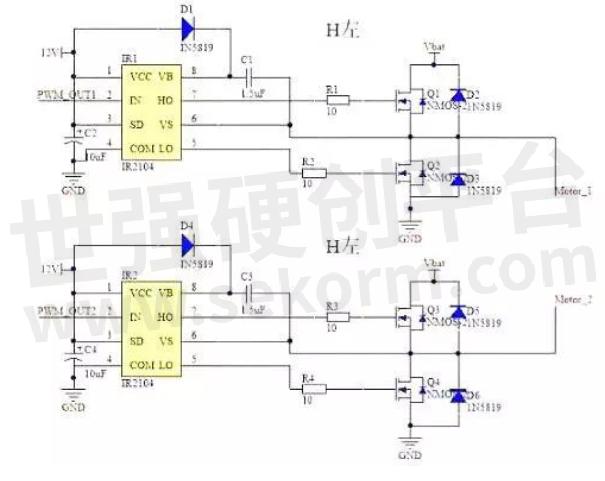
Fig.2
In addition, due to the driving circuit producing a larger injection current, to avoid impact on single chip microcomputer, it is better use isolated chips, there are many ways to isolate chip selection, such as 2801 and so on, these chips often do control bus driver, is driven to progress, after a certain condition, the output is the same as the input, can stop the data transmissions, the single chip microcomputer signal to drive chip, which in turn can't.
MOS tube H bridge motor drive circuit diagram
A typical DC motor control circuit is shown in Figure 3.
The circuit gets its name from the h-bridge drive circuit because it resembles the letter H. Four audions constitute the four vertical legs of H, and the motor is the horizontal bar in H (note: Figure 1 and the two subsequent figures are only diagrams, not the intact circuit diagram, in which the drive circuit of the audio has not been drawn).
As shown in the figure, the H-bridge motor drive circuit consists of 4 audions and a motor. To run the motor, a pair of transistors on the diagonal must be enabled. Depending on the conduction state of the triode pair, the current may flow through the motor from left to right or right to left, thus controlling the steering of the motor.

Fig.3
To run the motor, a pair of transistors on the diagonal must be switched on. For example, as shown in Figure 4, when the Q1 tube and Q4 tube are switched on, the current passes through the motor from the positive pole of the supply through Q1 from left to right, and then back to the negative pole of the supply through Q4. The current in this direction will drive the motor clockwise as shown by the current arrow in the figure. When triode Q1 and Q4 are on, the current will flow through the motor from left to right, thus driving the motor to rotate in a specific direction (the arrows around the motor indicate a clockwise direction).
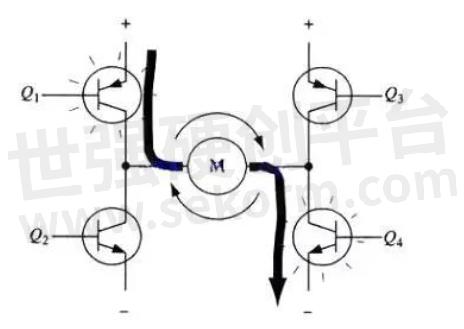
Fig.4
FIG. 3 shows the conduction of another pair of triodes Q2 and Q3, and the current will flow through the motor from right to left. When the transistor turns on Q2 and Q3, the current flows through the motor from right to left, driving the motor to rotate in the other direction (the arrows around the motor are counterclockwise).

Fig.5
Enable control and direction logic
When driving the motor, it is very important to ensure that the two transistors on the same side of bridge H do not conduct at the same time. If both Q1 and Q2 are switched on, the current will pass from the positive to the negative electrodes. At this point, there is no other load in the circuit except the transistor, so the current on the circuit may reach the maximum value (the current is only limited by the power supply performance), and even the transistor will be burnt out. Based on the above reasons, in the practice of driving circuits usually use hardware circuit local control transistor switch.
The modified circuit adds 4 gates and 2 non-gates to the base of the fundamental H-bridge circuit. The four are connected to the door with an "enable" signal so that the whole circuit can be switched on and off with this single signal. The two non-gates provide a direction input, which can ensure that at any time on the same side leg of the H bridge as long as a transistor can conduct. (Like the previous diagram in this section, FIG. 6 is not a perfect circuit diagram, especially when it is directly connected with the gate and triode, it cannot work normally).
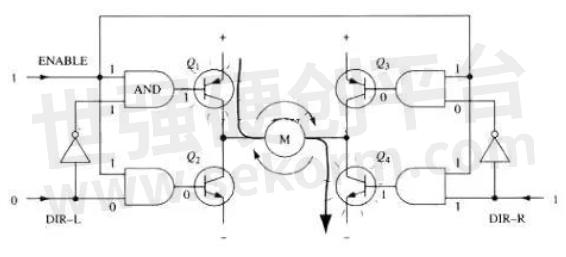
Fig.6
With the above method, the operation of the motor requires only three signals: two directional signals and an enabling signal. If dir-L signal is 0, the Dir-R signal is 1, and the enabling signal is 1, then triode Q1 and Q4 conduct on, and the current flows through the motor from left to right (as shown in FIG. 7); If the DIR-L signal becomes 1 and the Dir-R signal becomes 0, then Q2 and Q3 will be switched on, and the current will flow through the motor in reverse.
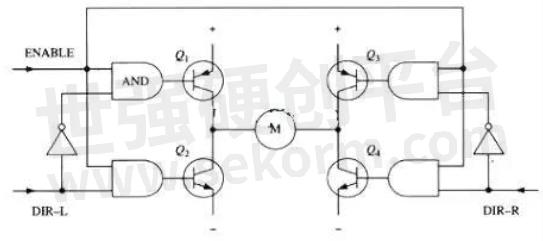
Fig.7
In practice, it is very difficult to make an H bridge with discrete components, but there are a lot of packaged H bridge integrated circuits in the market today, connected to the power supply, motor, and control signals that can be used, in the rated voltage and current is very easy to use. H bridge drive circuit with two discrete components:
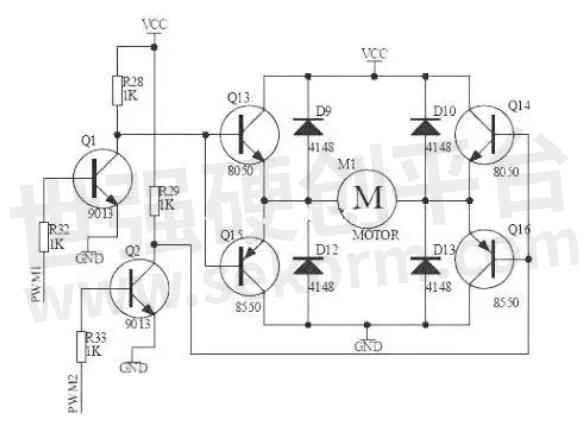
Fig.8
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Hi-semicon‘s 3A/500V N-Channel Enhancement Mode Power MOSFET SFF3N50TS and SFD3N50TS
- Hi-semicon‘s 5A/500V N-Channel Enhancement Mode Power MOSFET SFX5N50.H for PFC, SMPS,UPS and LED Lighting Power
- Hi-semicon‘s 10A/700V N-Channel Enhancement Mode Power MOSFET SFX10N70-Y for PFC, SMPS,UPS and LED Lighting Power
- MOS Tube and Simple CMOS Logic Level Circuit
- To Prevent MOS Tube from Burning, We Need to Know Why it Burns First
- The Popular Science, Why is the Channel Clipped in the Saturation Area of MOS Tube and the Current?
- Two kinds of structure of unit in SiC power MOSFET: plane structure and groove structure
- Solve the mystery of MOS tube damage
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































