DDR5 Fuels New Memory-Hungry Applications Latest Memory Standard Delivers 2X the Speed, 4X the Capacity, and Greater Power Efficiency Compared with DDR4

ATP ELECTRONICS launched the new Double Data Rate 5 (DDR5), the next-generation random-access memory (RAM) specification, is poised to exceed DDR4 in every way.
DDR5 promises faster performance, higher memory bandwidth, higher densities, and a new power management structure that delivers better power efficiency. All of these advantages, and more, are expected to meet the ever-growing memory needs of present and future applications.
Both DDR4 and DDR5 dual-inline memory modules (DIMMs) have 288 pins, but with DDR5's higher bandwidth, this means it can transmit data faster. While the pin count is the same, DDR5 DIMMs will not fit in DDR4 sockets as the alignment key is located differently and the pinouts have been changed to accommodate the new features.

DDR5 vs. DDR4 Alignment Keys
DDR5 Advantages Over DDR4
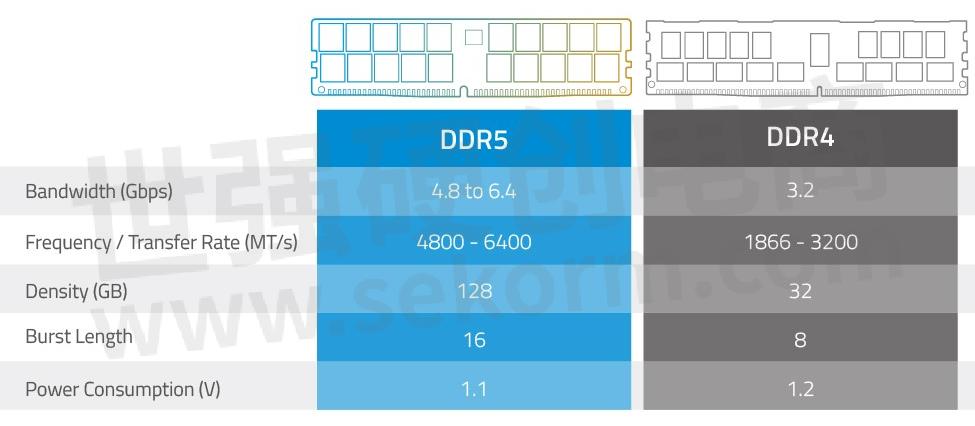
DDR5 vs. DDR4 Quick Comparison
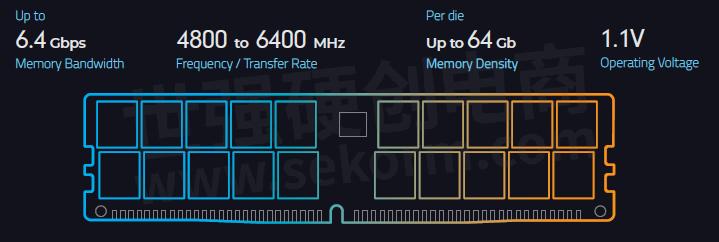
Memory Bandwidth
This refers to the theoretical maximum amount of data that can be transmitted (read/written) within a given time. Memory bandwidth is expressed in gigabits per second (Gbps). DDR5 memory bandwidth is initially at 4.8Gbps per pin, compared with DDR4's 3.2Gbps. Future versions are expected to double DDR4's, going up to a maximum of 6.4Gbps.
Frequency/Transfer Rate
Memory frequency refers to the number of commands or transfer operations that the memory module can handle per second. It is typically expressed in megahertz (MHz), but some manufacturers use express this in mega transfers per second (MT/s). The number follows the DDR version, so a DDR5-4800 DIMM, for example, has a frequency of 4800MHz (or 4800MT/s).
DDR4 frequency ranges from 1866 to 3200MHz, while DDR5 ranges from 4800 to 6400MHz initially, but may go as high as 8400MHz.
Memory Density
DDR4 maximum density is 16Gb per die, so with 16 dies, this translates to 256Gbit or a total of 32GB. DDR5, in comparison, has 64Gb per die, translating to 1024Gbit or a total of 128GB – this is 4X that of DDR4, enabling higher-capacity DIMMS!
Burst Length
This is the amount of data, which is input/output based on a single read/write command in DRAM. DDR5 doubles DDR4 burst length from 8 to 16, thus increasing the read/write efficiency.
Power Management and Consumption
The first power management IC (PMIC) on DIMM is introduced in DDR5. PMIC performs local voltage regulation on the module. Historically, voltage regulation has been done on the motherboard. PMIC on the module allows additional features such as threshold protection, error injection capabilities, programmable power-on sequence, and power management features (Source: Micron). DDR5's lower voltage of 1.1V compared with DDR4's 1.2V further reduces power consumption.
Summary: Important Spec Enhancements
The following table summarizes important enhancements of DDR5 from DDR4.

ATP Market Outlook
While many module houses started sampling 1st Gen. DDR5 to customers in 2021,the price gap at the functional level to justify the adoption for DDR5 over DDR4 is too wide to consider in ATP's view.
The following table shows that in the early stage, the price gap between DDR4 and DDR5 is over 50%. The transition may be slower than expected, but adoption is gaining traction. DDR5 is expected to become the dominant memory in the coming years as demand for faster memory with greater capacity and consuming less power is expected to expand and will not slow down anytime soon.
ATP is expecting significant market growth when processors and platforms supporting DDR5 become prevalent. With the release of Intel’s 12th generation Core hybrid processors supporting both DDR4 and DDR5, adoption is expected to increase steadily, even though motherboards will support only one or the other.

Insider Tips on Time-to-Market for DDR5
Price is key. Future die shrink and optimizer will lead to a better commercial situation for DDR5 adoption.
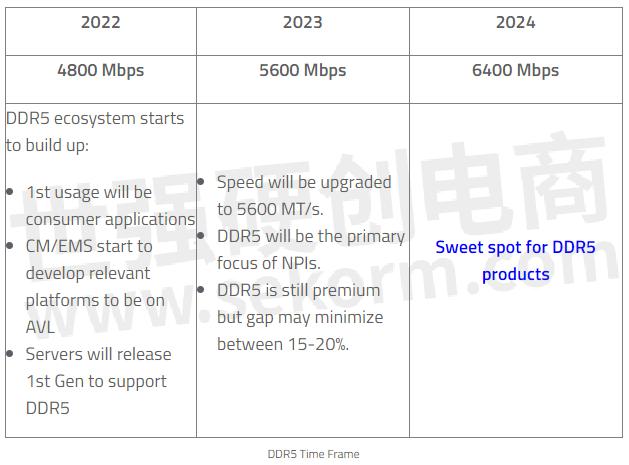
ATP is projecting that the DDR5 ecosystem will start building up within the first half of 2022 and new products will roll out.
While first usage will be in consumer applications, contract manufacturers (CMs) and electronic manufacturing services (EMS) will soon develop relevant platforms initially for approved vendors list (AVL).
By 2023, better adoption is expected, and speed will upgrade to 5600 MT/s. More new product introductions will focus on DDR5 and the price gap with DDR4 narrows down to 15-20%.
Finally, 2024 will be sweet spot for DDR5 products.The following table provides a summary of the DDR5 time frame.
ATP Electronics is committed to meeting the most rigid memory requirements of varied industries. The next-generation DDR5 memory modules are expected to deliver performance and reliability improvements over the previous generation, especially for critical computing applications.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- ATP Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT): Accelerating Failure to Maximize Reliability and Endurance
- News | NAND Flash Storage Solutions for the Data-Driven 5G Era | ATP
- ATP Electronics’ Latest pSLC Embedded SSDs Offer Best TCO with Customizable Endurance
- DDR5 vs DDR4: Is DDR5 finally necessary?
- ATP Exhibits at Embedded World 2024
- The ATP Gym and Coach System: Exercising SSDs to Ensure Total Fitness
- ATP‘s PCB Assembly Solderability Validation Tests
- New Die Package Extends 3D TLC e.MMC Endurance to MLC/SLC Levels of ATP E750Pi/Pc, E650Si/Sc Series e.MMC
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































