ATP Wide-Temp DDR4 RDIMMs with I-Temp Registered Clock Driver Ensure Maximum Reliability in Extreme Temperatures

Server systems running non-stop typically use registered dual-inline memory modules (RDIMMs) to meet the rigors of compute-intensive operations. Let us have a look at what RDIMMs are, why they are commonly used in demanding applications, and why wide-temperature capabilities are increasingly becoming a necessity.
Why RCDs are Critical Components of RDIMMs
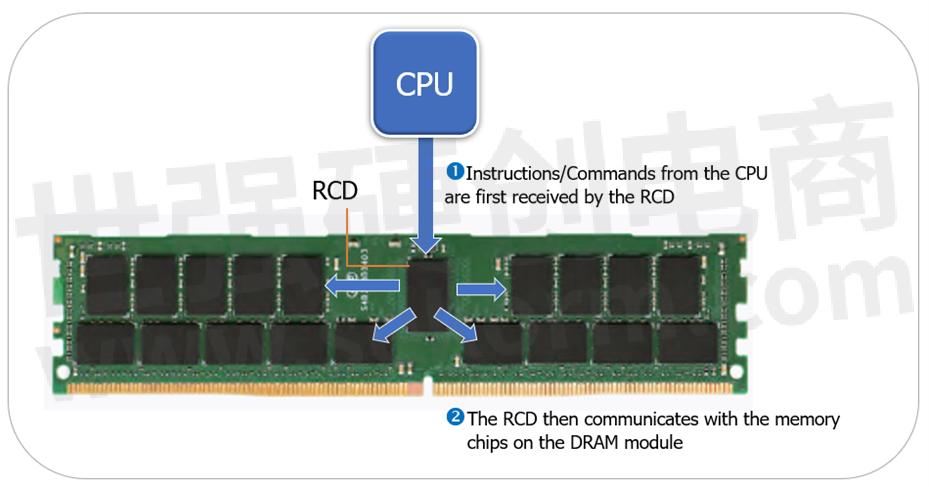
A registered clock driver (RCD) chip, simply known as a "register," is a critical component of RDIMMs. Its main function is to first receive the instructions or commands from the CPU before sending them to the memory modules. The RCD serves as a "mediator" between the CPU and the DIMM — the data signal stays on the RCD for one clock cycle, and then transfers from the RCD to the DIMM on the rising edge of the next clock signal. This results in instructions taking one CPU cycle longer, but the buffering reduces the strain on the CPU's memory controller and helps reduce the impact on signal integrity.
The main purpose of the RCD is to maintain the same memory speed even in heavy workloads. In contrast to speed-driven applications like gaming, enterprise systems and server applications require sustained performance as well as the high capacity and extra reliability features made possible by the RCD on DDR4 memory modules.
The figure below illustrates how the CPU communicates first with the RCD on each module, which in turn communicates with the memory chips on the dynamic random access memory (DRAM) module.
ATP's Wide-Temp RDIMMs with I-Temp RCD: Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Cold and Heat
It is not uncommon for DRAM modules to be installed in systems that operate in harsh environments and extreme temperatures that fluctuate during daytime and nighttime, as well as in varying weather conditions.
From land to sea, aerospace, and even outer space, applications in demanding computing environments require rugged, reliable, and enduring memory. For such demands, regular commercial-grade DRAMs rated to support temperatures from 0℃ to 85℃ may not be up to the challenges. When these memory modules fail, the time, labor, and cost required to replace them in remote locations can disrupt operations and adversely affect the business.
As edge computing for the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Artificial Internet of Things (AIoT), and 5G Open Radio Access Network/Distributed Unit (O-RAN/DU) becomes more universal, memory with a broader range of temperature capabilities is becoming more necessary than ever.
ATP recognizes that most edge computing applications run 24/7, often in challenging environments. To offer better endurance and redundancy in critical environments where commercial-grade DRAMs do not suffice, ATP offers DDR4 wide-temp RDIMMs with industrial-temperature-rated RCD.
The following table provides a comparison between commercial grade and wide temperature RDIMMs with I-Temp RCD, which offer stability and reliability even in sub-zero temperatures.
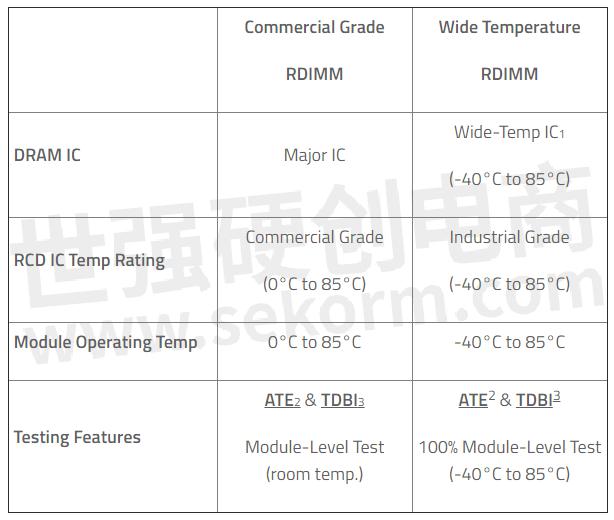
1. Wide-temperature ICs are ATP's best solution to reaching industrial-grade performance at lower cost through enhanced and more rigorous testing.
2. ATE: Automatic Test Equipment
3. TDBI: Test During Burn-in
ATP Reliability Testing
Like all ATP ELECTRONICS DRAM modules, ATP's wide-temp DDR4 modules with I-Temp RCD undergo rigorous 100% module-level testing to ensure maximum reliability.
• Functional Testing Using Automatic Testing Equipment (ATE). The ATE detects component defects and structural defects related to the DIMM assembly and screens out marginal timing and signal integrity (SI) sensitivities. ATE provides electrical testing patterns with various parameter settings, such as marginal voltage, signal frequency, clock, command timing, and data timing under a continuous thermal cycle. The ATE testing system can pinpoint individual defective ICs or DRAM PC boards, thus providing a more efficient failure analysis method for both new product development and mass production stages.
• System-Level Failure Detection and Prevention via TDBI. Through accelerated testing methods such as test during burn-in (TDBI), ATP significantly lowers failure rates and extends the product service life by making sure that only robust DRAM chips are on the module. Even just a 0.01% error on a 99.99% effective device can increase the failure rates at the module level and lead to failure in actual usage, TDBI detects and screens out up to 0.01% error to ensure the DRAM modules' reliability. TDBI testing may be tailor-fitted according to customer criteria, using various temperatures, power cycling, voltages, and other stress conditions within specified periods of time.

ATP TDBI combines temperature, load, speed, and time to stress test memory modules and expose the weak module.
Key Specifications
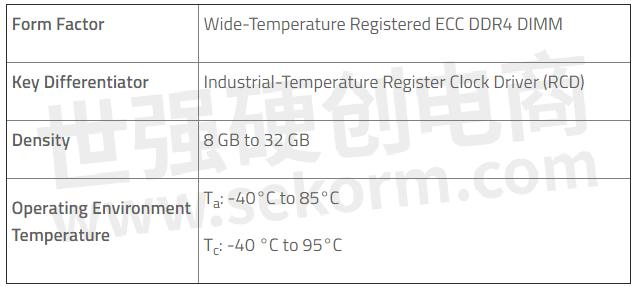
(Ta = Ambient Temperature; Tc = Case Temperature)
Conclusion
The increasing adoption of IIoT, AIoT, and 5G O-RAN/DU has been giving rise to more memory-intensive and memory-hungry applications, many of which are expected to run 24/7 in harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures. Commercial-grade DDR4 RDIMMs may not be up to the task and using them in rigorous scenarios may mean greater expenses in terms of operational disruptions and difficult, time-consuming replacements.
ATP's wide-temperature DDR4 DRAMs with I-Temp RCDs offer the best solutions, especially for applications requiring dependable, consistent, and enduring performance in extremely low and extremely high temperatures. Backed by over 30 years of manufacturing expertise and top-notch reliability testing, these rugged and reliable memory modules are built to withstand the most unforgiving environments.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- ATP Offers Rare 64GB DDR4 VLP RDIMMs with Twice Higher Density Enhancing Embedded Industrial and 5G IoT System Capabilities to Process Huge Amounts of Data
- The Advantages of High-Density VLP RDIMMs for Edge/5G/IIoT Applications
- DDR5 Value RDIMMs Provides Twice the Performance Compared to DDR4
- DDR5 Fuels New Memory-Hungry Applications Latest Memory Standard Delivers 2X the Speed, 4X the Capacity, and Greater Power Efficiency Compared with DDR4
- Can Your DRAM Withstand Wide-Temp Operating Conditions?
- DDR5 vs DDR4: Is DDR5 finally necessary?
- A Registering Clock Driver Used on DDR5 RDIMMs and LRDIMMs——Renesas RCD 5RCD0148HC2
- SMART‘s DDR4 Modules Range From 32GB To 4GB, 20% Lower Overall Power Vs. DDR3
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































