The Magic Behind RTK: Delivering Unparalleled Positioning Precision

In today's advanced technological era, accurate positioning has become a cornerstone for numerous applications, ranging from agriculture to construction and beyond. But what exactly is RTK, and how does it stand out in the vast landscape of satellite navigation systems?

1 Understanding RTK (Real-Time Kinematic)
RTK, or Real-Time Kinematic, is a satellite navigation technique fundamentally crafted to enhance the precision of position data procured from satellite-based positioning systems like GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou.
Imagine you're on a vast open field, trying to determine your position using a conventional GPS. Typically, you might get accuracy within a few meters. Now, introduce RTK into the scene, and suddenly, you're pinpointing your location with an incredible centimeter-level accuracy! This leap in precision is achieved by RTK's unique ability to correct GPS signals, thereby setting itself leagues apart from other positioning methods.
2 RTK vs. PPK: What's the Difference?
While diving into the world of high-precision satellite navigation, you're bound to come across PPK or Post-Processed Kinematic. On the surface, RTK and PPK might seem like twin siblings, but they have distinct operational differences.
The most significant distinction lies in the timing of data correction:
RTK: As the name suggests, Real-Time Kinematic provides real-time corrections. This means that as you move and collect data, RTK is continuously refining and correcting your position, giving you immediate, high-precision results.
PPK: Post-Processed Kinematic, on the other hand, is a patient player. Instead of offering real-time corrections, PPK collects raw measurement data in the field. After your data collection session, this data is then processed and refined post-mission, giving you your high-precision results afterward.
So, when deciding between RTK and PPK, it boils down to whether you need immediate precision as you go (RTK) or if you're okay with collecting data first and achieving precision later (PPK).
3 RTK Configuration
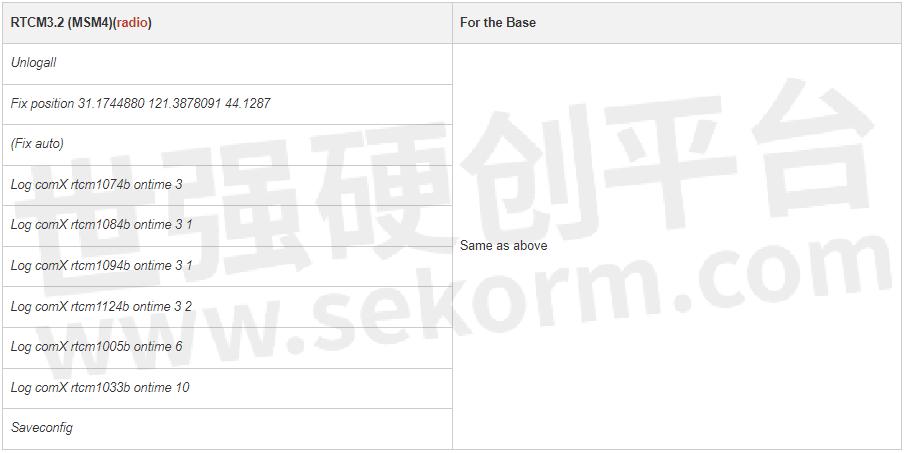
To achieve the most from RTK technology, correct configuration is imperative. The test was done using a K8 series GNSS module.Here are the recommended configuration steps based on RTCM3.0/3.2, the standardized message format for differential correction:

For the Base
Here are commands of RTCM with different formats, including RTCM3.0, RTCM3.2 MSM4, and RTCM3.2 MSM5.
If the use radio modem is for data link communication between Base and Rover, as considering limited data size can be sent per second, suggested to use of a subcontracting strategy for the base to transmit different constellations.
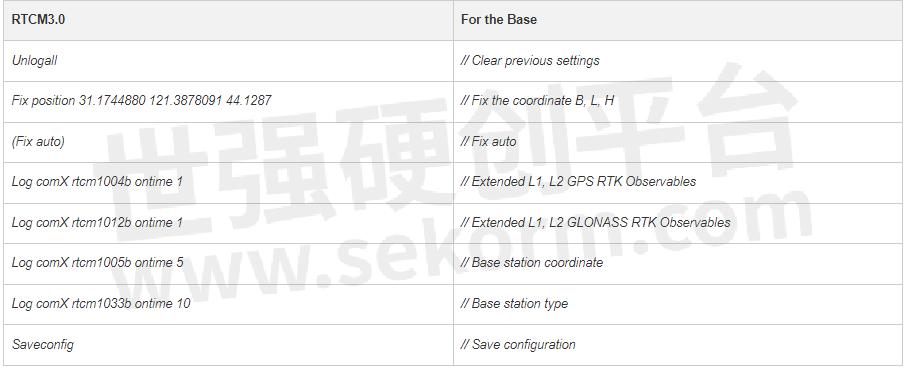
RTCM 3.0 includes only GPS and GLONASS, so no need to use a subcontracting strategy even using a radio data link.



For the Rover

Tip: If comX is the serial port used for configuration currently, please replace command saveconfig with interfacemode saveconfig.
Upon successful configuration, you can check the OEM board's mode with the `$GPGGA` message. If it's in RTK mode, the solution status should display as “E,4”. $GPGGA,015101.00,3121.0000551,N,12117.5483125,E,4,23,1.1,37.2598,M,0.000,M, 02,0004*58

Rover-RTK fixed
Moreover, the default setting is survey mode, and you will need to adjust to the correct dynamic mode according to your applications. For example the device used for land survey, you can use the default mode “survey”, if the device is used on robot, you will need to set the mode to “robot”. In different modes, the RTK engine treats the observation data in different styles to promote the performance of the RTK engine. The command is as below:

Conclusion
Understanding and correctly configuring RTK is paramount for professionals aiming for precise positioning. Whether you're new to this field or looking for a refresher, always remember to consult relevant manuals, and don't hesitate to explore more comprehensive resources online for in-depth insights.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Recommend Commands for System Integration
- How to Active the Event Option for Your GNSS Module K8 series from ComNav Technology
- ComNav‘s K8 Series GNSS Module can track the Galileo E6b signal and Has Verified the HAS Service in Most Countries
- Lighter, Thinner, Faster - ComNav Technology Introduced T20 Palm RTK
- How to Enable GNSS+INS System on ComNav K8 Series GNSS Modules
- ComNav Technology Launched GNSS High Precision Positioning Solution for Lawn Mower
- ComNav Technology‘s Z30 Portable GNSS Receiver: Precision in Your Pocket
- ComNav Technology‘s T300 GNSS Receiver: Decade Passed, Legend Still
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































