How to Enable GNSS+INS System on ComNav K8 Series GNSS Modules

GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) is a satellite-based positioning system that provides location and time information anywhere on or near the Earth's surface. Examples of GNSS include GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou.
INS (Inertial Navigation System), on the other hand, is a self-contained navigation system that uses accelerometers and gyroscopes to track the movement of an object. By measuring changes in velocity and direction, INS can calculate an object's current position and trajectory. INS is particularly useful in areas where GNSS signals are weak or unavailable, such as underground or underwater.
In many cases, GNSS and INS are used together to provide a more accurate and reliable navigation solution. This is known as integrated navigation or GNSS/INS integration. ComNav K8-series GNSS modules combine the strengths of both systems, integrated navigation can be robust in challenging environments and provides continuous positioning even during short GNSS outages, here are some examples of K8 GNSS+INS performance in different environments.
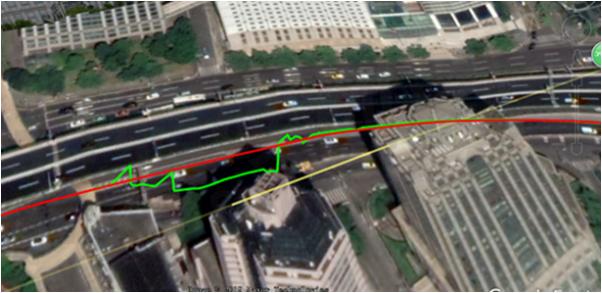
Under overpass
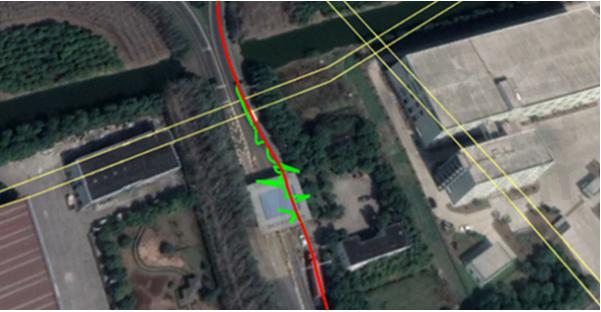
Through subway station
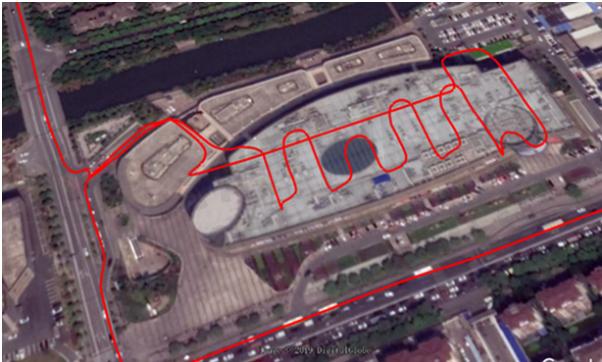
In the Garage
Installation and setup
1) Installation
Install the board on the vehicle as rigidly as possible to ensure that the board and the vehicle will not move relative to each other during driving. The device also needs to be installed in a location that minimizes the impact of vibration and electromagnetic interference.
2) Setup INS mode
After installation, you can activate the INS option as a command

It is recommended that the Y-axis marked on the module be kept on the same straight line as the direction of the carrier body, that is, Y-axis points to the forward direction of the vehicle. For the different directions of installation, you can refer to the below chart to set up the imuaxestype with the command below.
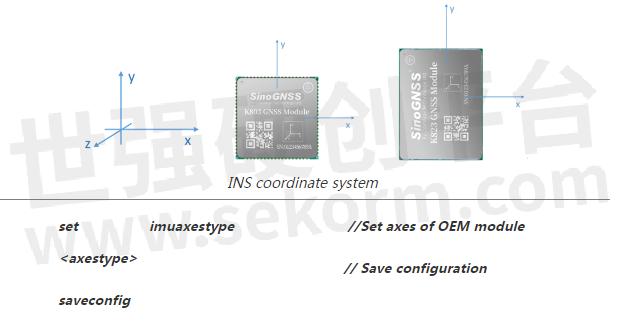
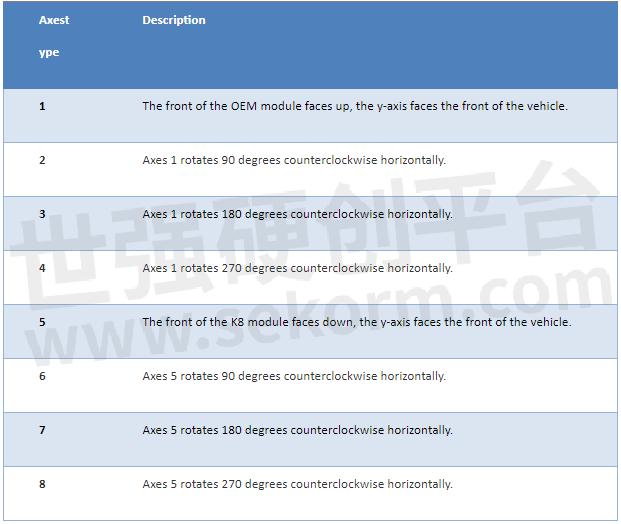
3) Setup Drleverarm value
Drleverarm value: the three-axis vector from the antenna phase center to the INS phase center.

Note: The XYZ is not related to the axis of INS. X points to the front of the vehicle, Y points to the right of the vehicle, and Z points downward.
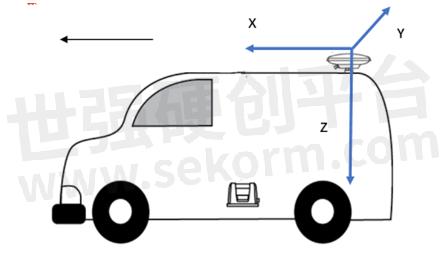
4) Save INS configuration
Once change the above INS configuration, it will need “reset” to the board to save the INS configuration.
INS Initialization
The inertial navigation system (INS) calculates the navigation result by integrating the measurement value of the inertial sensor, that is, each iteration of the navigation equation needs to use the previous navigation parameters such as position, velocity, and attitude as its initial value. Therefore, before using INS to provide navigation results, it must be initialized.
Method: After enabling INS, there will need first to get correction input to get RTK fixed solution, and then drive the vehicle to an open environment, make sure the speed reaches the initialization threshold, and drive about 10m to complete the initialization.
INS Calibration
In order to ensure the performance of INS, it needs to be calibrated after the initialization is completed to eliminate the placement error of the INS equipment.
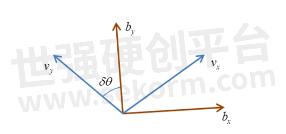
Method: Keep a speed of 5m/s in an open environment and drive in a straight line for at least 200m, turning 90° for left and right twice for each (with a good road environment, you can turn around in Figure 8).
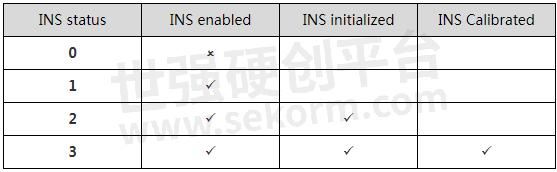
The status of calibration can be checked by the message “sysrts”. After calibrated, the status of INS will be “3”.

Here is a sample output of the SYSRTS message:
$SYSRTS,466724.10,093826.10,48,5,,AT,41,78,1,1,49,,,,,,,,,M,AIR,0,,42.5,3,9,2200,0,0*3A
There are totally 4 different types of status for INS, as the below table lists:
Positioning and heading message
Request positioning and heading message with GPGGA message and GPTRA message.

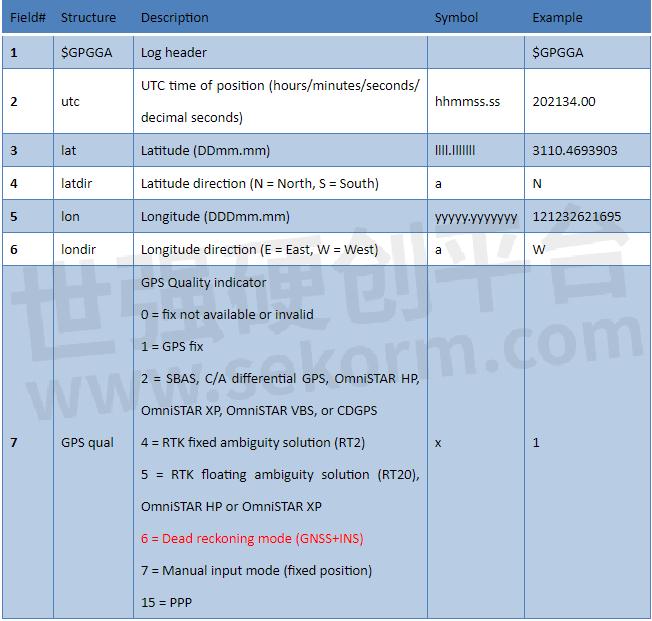
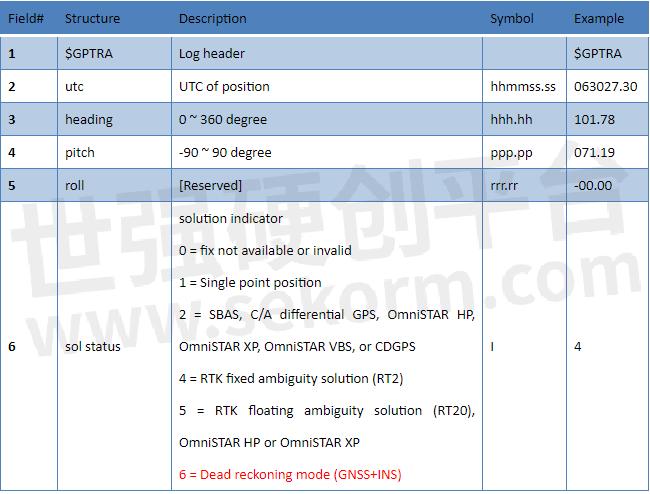
In the GPGGA message, the solution status for GNSS+INS is “6”; In the GPTRA message, the solution status for GNSS+INS is “6”.
Example of GPGGA message
$GPGGA,024941.00,3110.4693903,N,12123.2621695,E,6,16,0.6,57.0924,M,0.000,M,99,AAAA*55
Example of GPTRA message
$GPTRA,063027.30,101.78,071.19,-00.00,6,10,0.00,0004*51
About Comnav Technology
ComNav Technology is the major provider of GNSS OEM boards, receivers, and high-precision positioning solutions, encompassing product development, and marketing. Its technology and products have already been applied in a wide range of fields such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, and unmanned system. With its experienced team and innovational spirit, ComNav Technology is always trying its best to provide reliable and competitive products to global customers. In 2015, ComNav Technology was listed on the China National Equities Exchange and Quotations (NEEQ), Securities: ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation).
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in the People’s Republic of China, EU, USA, and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.













































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































