Quick understanding of LoRa & LoRaWAN

What is LoRa®?
LoRa uses unlicensed sub-GHz wireless bands such as 433MHz (Europe), 868MHz (Europe) and 915MHz (North America). It allows long-distance transmission (10km+ in suburbs, up to 2km in urban areas) and still maintains extremely low power consumption (sub-uA).
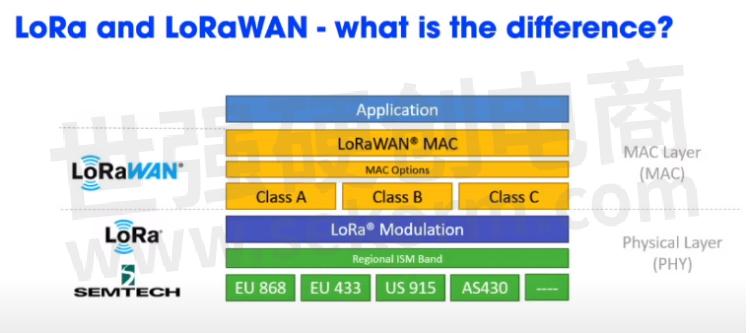
There are two expressions of this technology: LoRa, physical layer; LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network), upper layer.

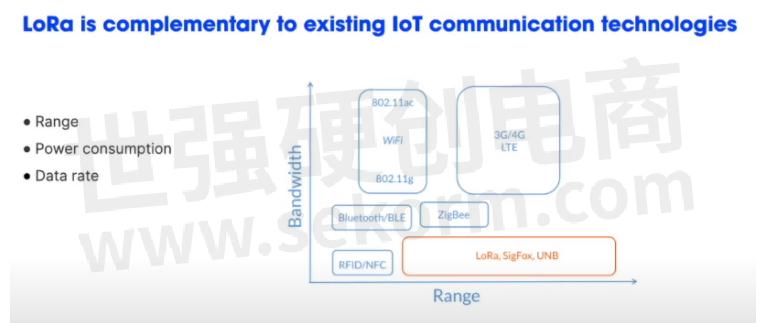
LoRa is a long-distance wireless communication technology that complements NB-IoT and LTE Cat N1 effectively. Compared with the traditional cellular technology, LoRa can reach the extreme distance range 100km+ LOS by sacrificing the data rate.
Due to rate limitations(<50kbps)and duty cycle limitations, LoRa is more suitable for non-real-time applications that can tolerate large delays.
LoRa is a physical layer technology that uses CSS (chirp spread spectrum) modulation. It was the first low-cost CSS implementation for commercial use.
LoRa can be used as an alternative solution for IoT in many different industrial application scenarios.
LoRaWAN Features:
Ultra-low power
Long-range
Deep indoor penetration
License-free spectrum
Geolocation
Public and private deployments
End-to-end security
Firmware updates over the air
Certification program
Ecosystem
LoRaWAN Use cases:
Natural disaster prevention
Smart agriculture & animal production
Endangered species protection
Smart industry control
Smart Cities, Homes, Buildings & Offices
Supply Chain Logistics, Asset Tracking & Quality Management
Smart Metering Facilities (Water, Gas, Electricity)
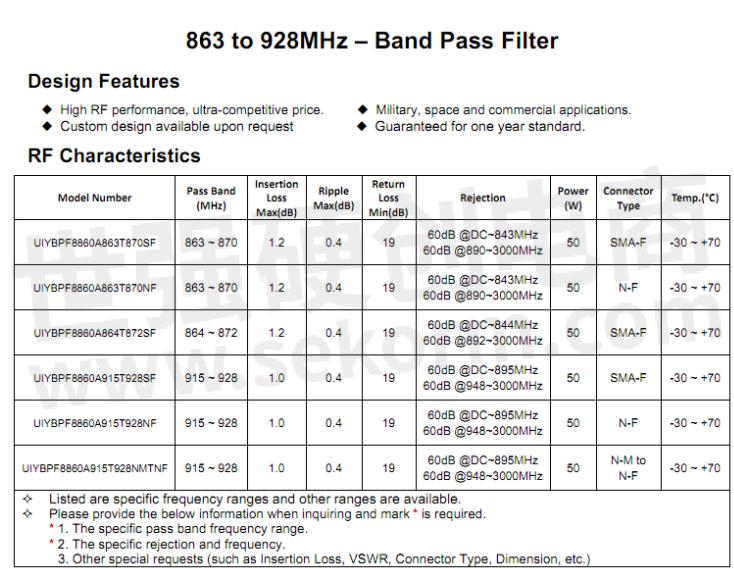
Network coverage:

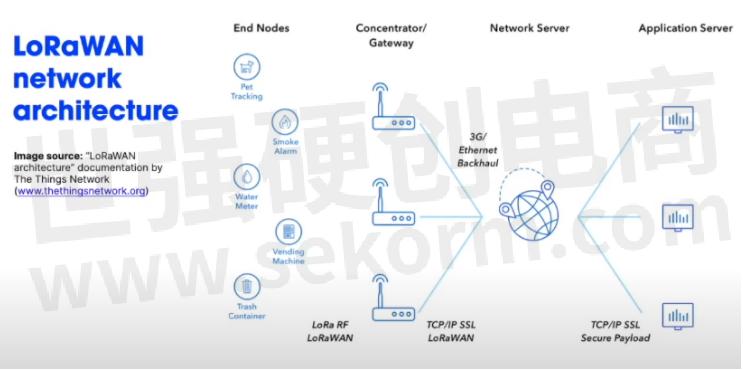
LoRaWAN network architecture:
What is the difference of Lora and LoRaWAN?
What is LoRaWAN®?
LoRaWAN is a protocol stack on top of LoRa. It is a media access control (MAC) layer protocol that plays the role of the network management protocol for LPWAN. It is responsible for sending information between gateways and end nodes.
The specification for LoRaWAN 1.0 was adopted in June 2015. It has been maintained by the LoRa Alliance ever since.
LoRaWAN defines the communication protocol and system architecture of the network, and the LoRa physical layer makes long-distance communication links possible.
LoRaWAN is also responsible for managing the communication frequency, data rate, and power of all devices. When the device needs to send data, the device transmits asynchronously. Data sent by a device of an end node can be received by multiple gateways, which send the data packet to a central network server. The web server filters duplicate packets, performs security checks, and manages the network. The data is thus sent to the application server.
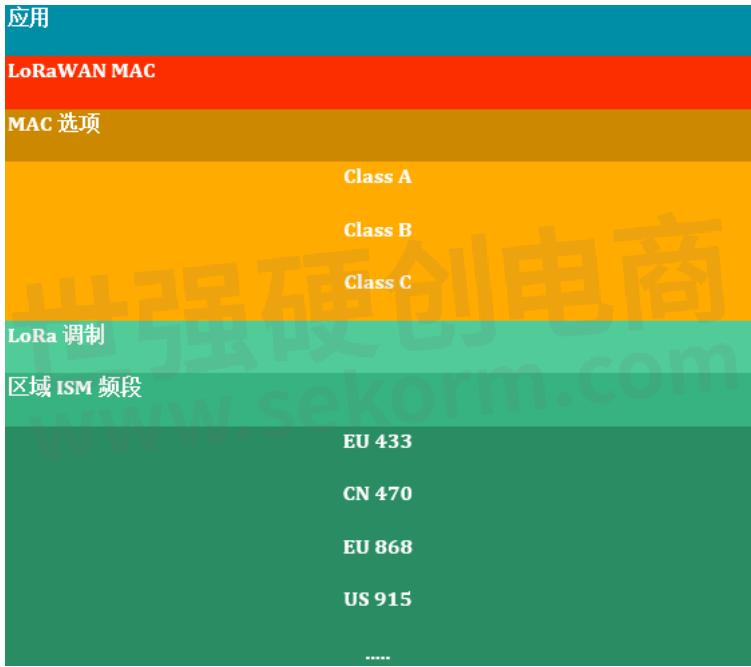
Figure: LoRa application stack.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Installation of UIY Surface Mounting Isolator/Circulator
- UIY Released New 180° 3dB UIY2T2HC4040A, Operating Over 6-18GHz Ultrawide Band, Insertion Loss Less Than 1.5dB
- UIY INC. Exhibits at 2024 IMS Washington D.C. 18th~21th June
- 5 Clues Help Understanding the DBS Band
- Things You Need to Know About Combiner and Duplexer
- Frequency Bands Suitable for Satellite Communications
- Microstrip Isolator/Circulator Mounting Instruction Manual
- Installation Instruction of Drop In Isolator & Circulator
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































