In Thermal Design, Which Design Elements can Engineers Optimize to Achieve Effective Cost Reduction?

In heat dissipation design, adopting effective cost-reduction methods can improve the reliability and efficiency of the overall system while reducing unnecessary costs.
1. Derating design reduces costs
Derating design is a design method that intentionally reduces the electrical, thermal and mechanical stresses that components or products are subjected to during operation. In actual production and use scenarios, the stability of electronic equipment can be improved by reducing the stress borne by components.
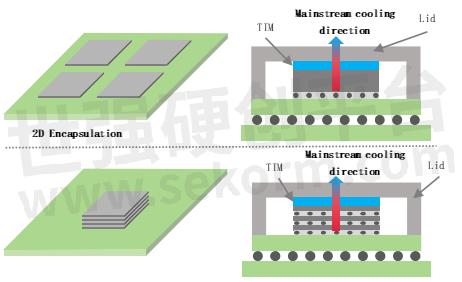
Schematic diagram of heat dissipation paths for 2D and 3D packaging
Reduce working stress: During product design and operation, the working stress of components can be reduced by reducing the workload, controlling the operating frequency, limiting the current and voltage, etc.
Reduce environmental stress: Reduce environmental stress by selecting appropriate component types, layouts, and packaging forms, such as selecting components with a large temperature margin, or using packaging forms with good sealing to reduce the effects of temperature, humidity, and pressure on components.
Reliability engineering application: reasonable redundant design, fault detection and isolation, etc., further reduce the failure risk of components.
By reducing the stress on components during operation, their power consumption and heat generation can be reduced. When power devices operate under stress conditions lower than their rated stress, their power consumption and heat generation can be reduced, which helps to improve the energy efficiency and reliability of the system. In the long run, derating design effectively increases the life of components, reduces failure rates, reduces maintenance workload, and thus reduces costs.
2. Optimize layout
The working efficiency of the radiator can be significantly improved through reasonable arrangement of thermal components, and a reasonable component layout strategy can achieve a balance between product performance and cost.
Distribute heat dissipation components: Disperse components that generate large amounts of heat to reduce the heat load per unit area.
Location that is conducive to heat dissipation: Place the heating element in a location that is conducive to heat dissipation, such as near a vent or the edge of the device.
Staggered arrangement: During layout, stagger the heating components with other general components, and try to make the heating components principle temperature-sensitive components to reduce their impact on the heat-sensitive components.
Improve airflow: By changing the direction design and component layout, the airflow path is optimized, the flow rate is increased, and the heat transfer coefficient is improved.
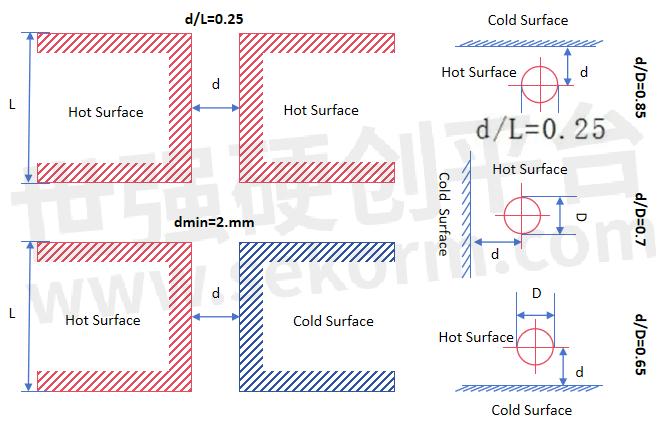
Spacing recommendations between components
3. Choice of cooling method
As the performance of electronic components improves and the degree of integration increases, the power density continues to increase, resulting in a significant increase in the heat generated by the electronic components during operation. When choosing a heat dissipation method for electronic components, the temperature control requirements mainly include the following aspects:
Temperature range: Different components have different temperature tolerance ranges. For example, high-performance chips such as CPUs have operating temperature requirements between 85-100°C, while some low-power devices can tolerate higher temperatures, so the cooling system must ensure Components operate within a safe temperature range.
Temperature control accuracy: In some scenarios with strict temperature control requirements, it is necessary to adopt a heat dissipation solution that can accurately control the temperature to avoid component performance degradation or even damage caused by excessively high or low temperatures.
Ambient temperature: The heat dissipation effect of electronic equipment not only depends on the heat dissipation capacity of the device itself, but is also affected by the surrounding ambient temperature. The heat dissipation design needs to consider changes in ambient temperature and try to keep the device within a suitable temperature range through heat dissipation means.
Power consumption and reliability: Some low-power electronic components can use natural heat dissipation when they generate low heat. For high-power consumption equipment, it is necessary to wait for the heat dissipation technology of universities to ensure that it maintains normal performance and prolongs operation under high load. service life.
Sealing and density: In sealed and high-density assembled devices, if the heat generation is not high, you can rely on natural heat dissipation. When components are densely packed and generate large amounts of heat, more effective heat dissipation technologies such as forced heat dissipation or liquid cooling are needed. Liquid cooling and heat pipe technology are used in scenarios with high power consumption and large heat generation, such as high-power electronic components such as traveling wave tubes, magnetrons, and power amplifier tubes, servers and high-power consumption equipment, and three-electric systems of new energy vehicles.
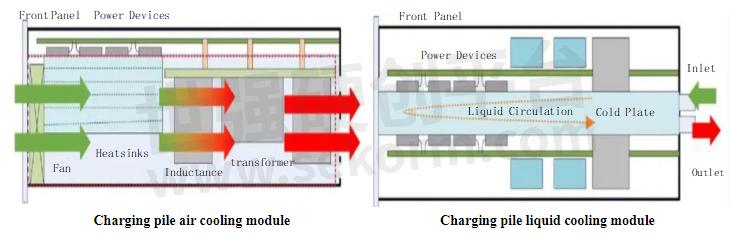
When choosing a cooling method for electronic components, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as heat generation and heat flux, ambient temperature and operating temperature, space constraints and thermal isolation requirements, and cost and feasibility. By using appropriate cooling technology and cooling devices to ensure that components operate at a suitable temperature, the cost of system replacement and maintenance can be effectively reduced. In addition, reusing historical projects is also an effective strategy to reduce development and manufacturing costs and improve reliability.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Which Type of Radiator is Generally Used in Computers?
- The Innovation for 4 heat Pipes CPU Radiator of High Cooling Performance 220W
- What is a Heat Sink Radiator: Unveiling the Secret of Efficient Heat Dissipation
- Why Would The VC Radiator Been Famous?
- BOYD‘s Electric Vehicle Radiator Cooling Solution
- Is the Poor Performance of the Radiator a Problem with the Thermal Material?
- Renesas Completes Acquisition of Steradian
- Do 4g Industrial Router Emit Radiation?
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.



























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































