A Brief Discussion On The Use Of Current Sensors - Taking XBLW GT712 As An Example


Customers often ask how our current sensor works, how to choose the range, and whether the chip will be burned out if the current exceeds the standard. In response to customer questions, I believe that after reading this chip knowledge sharing article, you will roughly understand how this chip is used.
1. What is a current sensor chip
Firstly, in simple terms, a current sensor chip is a small chip that can sense and report the flow of current. It is like an 'eye' in our circuit, used to observe and monitor the flow of current. Whether in industrial production, electronic power, automobiles, or our household electronic devices, these small components are silently playing a role.
2. How does it work in the circuit
When it comes to how a current sensor works, first of all, we need to know its working principle. Generally speaking, this type of chip works by detecting the current passing through the sensor. But when it comes to implementation methods, there are mainly several different technical paths.
2.1. Sensor based on Hall effect
Hall effect sensors are a very popular technology. In short, when current passes through a conductor, if the conductor exists in a vertical magnetic field, a transverse voltage will be generated on both sides of the conductor, which is the Hall effect. Our XBLW GT712 current sensor chip is based on this point, which calculates the magnitude of the current flowing by measuring the lateral voltage. The advantage of this method is that it can achieve non-contact current measurement, which will not affect the circuit itself.
2.2. Resistance current sensor
Another common technique is to measure current by detecting the voltage drop across a resistor. You may remember Ohm's Law, which states that when a current passes through a resistor, there is a voltage drop that is proportional to the current. The current sensor chip can calculate the magnitude of the current by accurately measuring this voltage drop. This method is simple and direct, but it may have some minor impact on the circuit itself as it requires inserting resistors into the circuit.
2.3. Magnetic electric induction current sensor
Another way is to utilize the characteristic of electric current to generate a magnetic field. Simply put, when current passes through a wire, a magnetic field is generated around it. The current sensor chip can calculate the magnitude of the current by detecting this magnetic field. This method can also achieve non-contact measurement and is very suitable for high voltage or high current situations.
3、 Key introduction
Characteristics of XBLW GT712LBDTR Current Sensor
1. Chip Level Hall Current Sensor, connected in series in the current circuit, with a simple peripheral circuit.
2. Can measure AC and DC currents.
3. No need to detect resistance, built-in milliohm level path internal resistance.
4. Single power supply, the primary side does not require power supply.
A high bandwidth of 5.120KHz, with adjustable bandwidth and noise relationship through peripheral filtering capacitors.
6. The isolation voltage of the whole machine is 2500V
7. Overall output response time: 4μs (typical value)
8. Strong anti-interference ability of the whole machine, strong resistance to mechanical stress, and magnetic field parameters. The whole machine is resistant to mechanical stress and magnetic field parameters are not affected by external pressure movement
9. RoHS certification for the entire machine: (EU) 2015/863
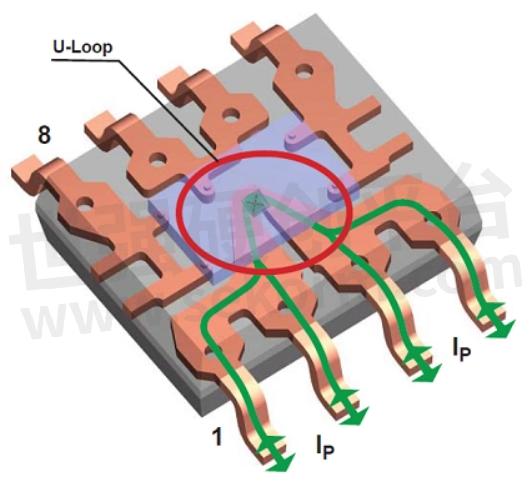
From the package anatomy diagram, it can be seen that the primary current only flows through the interior of the chip and does not make contact with the secondary circuit. The primary and secondary sides are isolated, and due to the small package size, the isolation voltage of XBLW GT712 is 2500V. Because the flow of current generates a magnetic field, Hall elements induce a linear voltage signal based on the magnetic field. After internal amplification, filtering, and chopper circuits, a voltage signal is output.
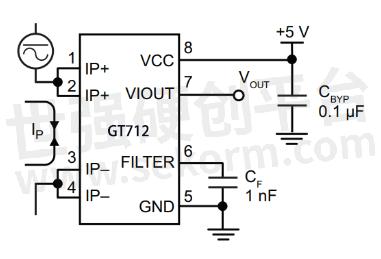
XBLW GT712 Typical application circuit
The
accuracy of XBLW GT712 over the entire temperature range is ± 1.5%. At
25~85℃, the accuracy characteristics are better. The response time
between input and output is 4us. The bandwidth is 120KHz. By adjusting
the filtering capacitor between the filtering pin and ground, the
relationship between noise and bandwidth can be adjusted according to
customer requirements—a larger capacitor value results in a smaller
bandwidth and lower noise. The XBLW GT712 is divided into three
specifications based on the suffix: 5A, 20A, and 30A, with temperature
levels ranging from -40 to 150℃. The input and output have a good
linear relationship within the range, with sensitivity coefficients of
185, 100, and 66.6mV/A, respectively.
4. The purpose of current sensors
What are the major uses of flow sensor chips? Their importance cannot be underestimated. From ensuring the safe operation of our household appliances to monitoring the current status of industrial equipment to prevent overload, current sensor chips are everywhere, constantly protecting our safety and ensuring the stable operation of our devices.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- XBLW High-Performance Hall-Effect Current Sensor GT712 with Operating Voltage of 4.5V~5.5V and Isolation Voltage of 2500V
- XBLW Showcased Linear Voltage Regulator XBLW AMS1117, RS-485/RS-422 Chip MAX3485 and Other Product in 2023 ES SHOW
- Application Of XBLW Products On Fascia Guns
- Xinbole (XBLW) Attended the Shanghai Munich Electronics Show, July 8-10, 2024
- XBLW LM2576S Series Is A New 3A Current Output Buck Switch Regulated Integrated Circuit
- Real-Time Clock (RTC) Chips XBLW DS1302 & DS1307: Powerful And Reliable
- 20V 5A DC Bidirectional Motor Driver Circuit Chip - XBLW CP2119, with A Working Voltage Range of 3V to 20V, Compatible for SS6285L
- Programmable Resolution Single-Bus Temperature Sensor - XBLW DS18B20 Offers Temperature Measurement With A Resolution of 9 To 12 Bits
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































