LoRaWAN Network Protocol Defines Three Operational Modes: Class A, Class B, and Class C

LoRaWAN is a low-power wide-area network protocol designed specifically for wide-area IoT applications. It is particularly suitable for IoT devices, enabling long-range communication at low data rates. The LoRaWAN network consists of multiple components, including nodes (end devices), gateways, and network servers. In the LoRaWAN network protocol, LoRa refers to the physical layer modulation technology, while LoRaWAN defines the rules and data formats for communication between devices.
The three working modes of LoRaWAN
The LoRaWAN protocol primarily defines the communication of IoT devices in low-power wide-area networks. It features three working modes: Class A, Class B, and Class C, each differing in power consumption, latency, and communication frequency to accommodate various application needs.
Class A Mode: Class A mode is the lowest power consumption mode and the basic mode for LoRaWAN devices. Devices can transmit data to the gateway at any time. After transmitting data, the device opens two temporary windows to receive the transmitted data. If no data is received in these windows, it waits until the next data transmission. Devices in Class A mode spend most of their time in a sleep state, consuming power only during data transmission and reception windows. This mode is suitable for applications with infrequent communication needs, such as environmental monitoring sensors.
Class B Mode: Building upon Class A, Class B mode introduces synchronized slots, allowing devices to open receive windows at scheduled times for gateway-initiated downlink transmissions. Devices periodically receive synchronization signals from the gateway, enabling them to open additional receive windows at specified intervals. This mode consumes slightly more power than Class A because devices need to periodically receive synchronization signals and open receive windows at scheduled times. It is suitable for applications requiring periodic communication or lower latency.
Class C Mode: Class C mode offers the lowest latency but consumes more power, suitable for applications requiring real-time communication or continuous monitoring. Devices can transmit data at any time and immediately switch to receive mode after transmission. Devices remain in receive mode almost constantly, closing the receive window only when transmitting data. Due to the constant receive state, this mode consumes more power and is suitable for devices with continuous power supply. It is ideal for applications needing frequent communication or low latency, such as industrial monitoring and smart lighting systems.

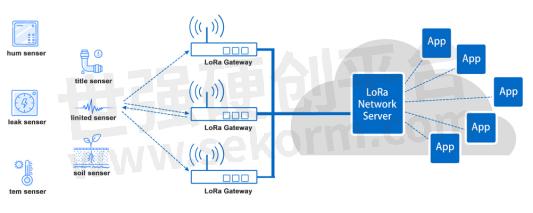
NiceRF LoRaWAN gateway
LG1301-PF is a LoRaWAN gateway. It can be used with any LoRaWAN nodes compliant with the standard LoRaWAN protocol V1.0. The gateway is hosted on a Linux platform and consists primarily of a concentrator, GPS module, WiFi, and Ethernet. The GPS module sends NMEA frames containing time and geographic coordinate data to the host. Additionally, the GPS module outputs a pulse to the sx1301 every second. The gateway receives RF data from nodes and forwards it to the server. It also receives data from the server and transmits it to the nodes. The gateway connects to the server via Ethernet or WiFi.
LN610 is a LoRaWAN node module. LG1301-PF/LG1301-SE are LoRaWAN gateways. LN610, together with LG1301, forms a LoRaWAN system. This LoRaWAN system integrates LoRaWAN V1.0 protocol and supports Class C. When data is input to LN610, LN610 transfers the data to LG1301. Upon receiving data from LG1301, LN610 outputs the received data through serial interfaces. All wireless communications adhere to the LoRaWAN protocol.
LG1301-PF or LG1301-SE can be used in conjunction with LN610.

LG1301-PF Features
LoRaWAN protocol supported
Uart interface
AES128 encryption
8 channel communication simultaneously
Configurable parameters
GPS support
Long range
EU433M / EU868M / KR920M / AS923M / CN780M/ CN470M / US915M / AS915M
Application
Smart city
Smart Metering ( Water, Electric, Gas meter )
Agricultural Monitoring
Irrigation control
Internet of Things (IoT)
M2M
Wireless Sensors
Wireless Alarm and Security Systems
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Data Security and Precision Control: Precision Application of Smart Irrigation Using LoRa Technology and LoRaWAN Gateway
- What Features Should a Portable Walkie-Talkie Module Have? Take G-NiceRF SA828 for An Example
- The Gas Meter Reading Application of RF Module RF4463Pro from G-NiceRF Saves Much Person Resource
- Advantages of G-NiceRF ASK Transmitter STX883Pro and ASK Receiver SRX883Pro in the Market
- G-NiceRF BLE5201 Module Communication Distance Testing Reaches 150m
- G-NiceRF LoRa1121 Module Newly Released: Enables Multi-Band Compatibility and Satellite Communication Functionality
- G-NiceRF LoRa Backscatter Device LoRa1276-C1 Provides Long-Range Communication with Low-Power
- G-NiceRF‘s FCC Certified Products for Wireless Transceiver Module: LoRa1276-915, RF2401PRO, RF2401F20, RF4463PRO
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.






























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































