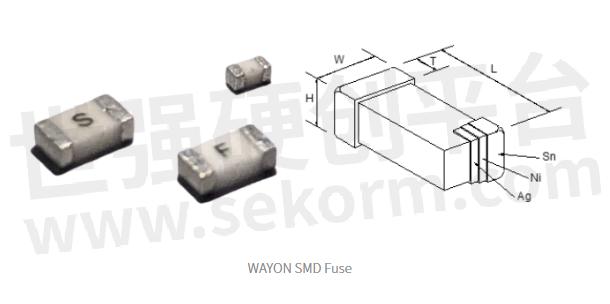
WAYON SMD Fuse Covering a Current Range of 0.25-40A : Security Guards for Portable Electronic Devices

A fuse is also known as a current fuse and is defined in IEC 127 as a "fuse-link", which is mainly used for overload protection. The characteristics of the circuit itself will lead to the existence of unstable abnormal currents in the circuit. The fuse will increase in temperature as the current increases, and when its own temperature reaches the melting point, it will melt and cut off the current to ensure the safe operation of the circuit. With the popularization of small electronic products, fuses are becoming miniaturized and surface-mountable. SMD Fuse has been widely used in the field of overcurrent protection of computer and peripheral interfaces, TVs, LCD monitors, mobile phones, rechargeable battery packs, and other portable electronic equipment(portable electronic devices).
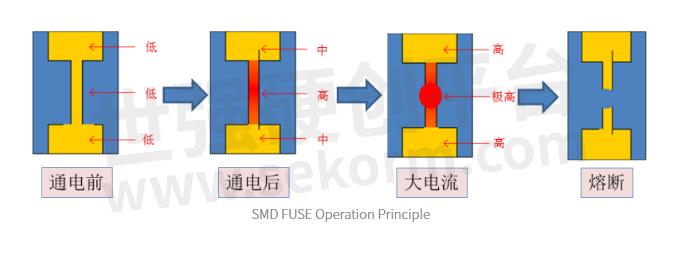
Chip fuse, like conventional fuse, generates heat through current to achieve melting. A fuse, connected in series in the circuit, generally requires its resistance and power consumption to be small. When the circuit is working properly, it is equivalent to a wire and can conduct the current steadily for a long time. When there is a large overload current in the circuit (fault or short circuit), the conductor heats up and follows Q=I²Rt. The heat generated per unit of time is greater than the heat dissipated, leading to an overall temperature rise of the fuse. When the temperature reaches its melting point, it will fuse, thus protecting the circuit.
Here's how it works: When the fuse is on, its resistance converts electrical energy into heat, which heats up the fuse. The heat generated by the current radiates to the surrounding environment through the fuse and shell and dissipates heat through convection and conduction. When the current through the fuse reaches a certain value, the heat converted by the electrical energy increases. The heat dissipation rate cannot keep up with the heat generation rate. The heat will gradually accumulate in the fuse, making the temperature of the fuse rise. When the temperature reaches the melting point of the fuse, the fuse begins to melt and continues to absorb heat, which causes further melting into a liquid state. The fuse temperature then rises further to the vaporization point to form an arc.
Arc is a gas-free discharge phenomenon, the strength of the arc is related to the voltage of the circuit, the higher the voltage the stronger the arc. The rated voltage of the fuse and the circuit voltage that the fuse can withstand when it melts is different, the fuse cannot be used in a circuit with a voltage higher than its rated voltage because the arc cannot be extinguished easily in this case. In addition, the intensity of the arc is also related to the current in the circuit, the greater the current, the stronger the arc. If the arc is not extinguished in time, not only the circuit cannot be cut off, but also other parts of the circuit may burn, thus leading to fire and causing accidents. The fuse will truly cut off the current only after the arc is extinguished, so as to protect other devices.
WAYON chip fuse has made structural and technological innovations on the basis of conventional chip fuse. The internal fuse is made of alloy material, combined with the screen printing process, the fuse is deep inside the substrate and sintered with the substrate material to form a solid whole, which greatly improves the arc extinguishing performance and reliability of the fuse. At the same time, it has excellent electrical properties. WAYON can adjust the product type (e.g. fast-acting fuse and time-lag fuse) by adjusting the screen pattern and fuse material. The finished products are inspected to ensure that the resistance value of each piece is qualified, and the finished products inspection includes several times of current action time limit, etc. The test results are reliable and certified by UL and TUV.

The flat bottom surface is suitable for surface mounting and the excellent end strength ensures good solderability. As a new type of thin and light component, chip fuse is used in various types of compact, small-sized electronic products, especially common in fashionable digital handheld electronic devices. As a protection component used in portable electronics, fuses must not only ensure abnormal currents are cut but also avoid misfusing of normal surge currents in the circuit. WAYON SMD fuse includes both fast-acting fuse and time-lag fuse series, covering a current range of 0.25-40A and withstanding voltages up to 400V. WAYON SMD fuse is available in several sizes for a wide range of circuit protection.

- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- The Advance of WAYON Domestic IGBT, with higher power cycle life and higher robustness
- Preferred Power Solution: Wayon VDMOS Offers High Versatility and Durability
- WAYON Offers the Bridgeless 240W Power Module Solution with Both High Power and High Energy Efficiency
- Booster in the Field of Adapters -- WAYON Power Schottky Diodes with Voltage Ranges from 45 to 200V
- WAYON Launches AEC-Q100 Automotive Grade 8-bit MCU – WY8A8503
- WAYON‘s 500V-1500V, Current Covering 2A~40A VDMOSFET for More Power Control
- Diverse Specifications, Flexible Packaging: WAYON‘s Thyristors Meet Your Various Needs
- The “Magic Bullet“ for High-Current Scenarios, the Advantages of WAYON TOLL MOSFETs Explained
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































