What Are the Key 5G Features Enabling 5G Private Networks for Industry 4.0?

5G private networks are proliferating. Revenue from 5G private networks will grow from $1.6 billion in 2021 to $65 billion in 2030. But the road to 5G private networks is paved with challenges that span all stages of the network lifecycle, from deployment to operations. In this paper,Keysight will tell us What Are the Key 5G Features Enabling 5G Private Networks for Industry 4.0?
Enabling 5G private network use cases, especially for Industry 4.0, demands high network performance. All network components must operate at peak performance and end-to-end network performance be optimal. Only testing the RAN network during site acceptance create blind spots.
Overcoming these challenges requires a strong understanding of 5G private network use cases and their requirements. You also need to be familiar with the underlying standards, deployments options, and the key 5G features enabling these networks.
Multi-access edge computing (MEC), time-sensitive networks (TSN) and 5G system security features are essential for enabling 5G private networks for Industry 4.0 use cases. MEC provides the 5G system with real-time awareness, TSN enables the connection of industrial devices to a mobile network and provides the ability to control them, and the security features of the 5G architecture increase the private network's security.
Mobile-Access Edge Computing (MEC)
MEC brings computation capability physically closer to the user and helps achieve lower latency. MEC also enables offloading computing demands from devices that need a lot of compute resources like augmented reality (AR) glasses and wireless robots. It enables offloading the computing requirements from these devices to an edge computer using a 5G data link and make the glasses/robots lighter and more energy efficient.
Figure 1 shows an example of an AR device using a 5G private network. AR glasses will help increase worker safety, provide remote support, and help train workers in an increasingly complex environment, among other benefits. In this example, a camera integrated into an AR device takes images and sends them to a processing server. The processing server determines the current field of view of the camera and the optimal placement for the augmentations registered previously in the current image. It then renders the augmented image and sends it back to the AR glasses to display. Augmentations in the view field need to follow the movements of the AR device closely without introducing distortions. This use case requires significant computational capabilities, high uplink and downlink data rates, and low latency.

Figure 1. Example of a 5G private network leveraging edge computing for an AR use case (Source: Korea Electronics Technology institute)
Time-Sensitive Networks (TSN)
TSN support is another important feature for 5G private networks. This feature is a key enabler for factory automation. The low-latency features built in 5G can create an end-to-end time-sensitive communication channel that spans a whole infrastructure.
Many 5G private networks will be deployed in existing factories with a wired communication infrastructure in the process of adopting wired TSN. Translating wired TSN capabilities into 5G (and vice versa) is important for enabling Industry 4.0 applications. Figure 2 provides a typical 5G architecture supporting TSN.
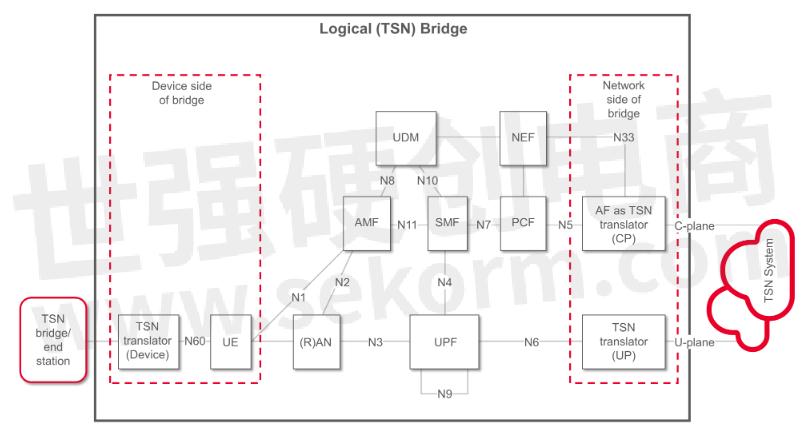
Figure 2. 5G network with TSN support
Security
Security is another important aspect to take into consideration in the deployment of a 5G private network. The 5G architecture (Figure 3) includes significant security enhancements compared to previous generations of cellular technology including more capable and secure encryption and authentication systems.
The 5G network architecture is designed to take the security measures necessary for the different services a network provides, whether it be a voice call, the control of a robotic function, or collecting data from hundreds of sensors.
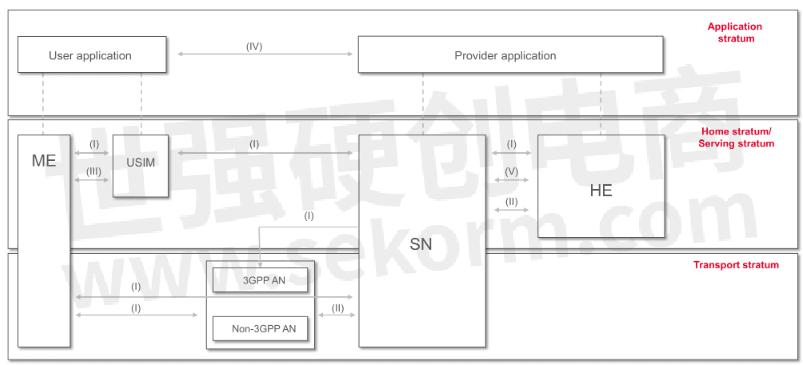
Figure 3. 3GPP 5G security architecture
The Rise of 5G Private Networks
The adoption of 5G in the manufacturing sector is increasing. In a recent survey with senior executives from 1,000 industrial organizations, 30% said they were at the piloting stage or beyond and 40% expected to roll out 5G at scale at a single site within the next two years.
In addition, many companies (64%) said they planned to adopt 5G-based edge computing services within the next three years and more than a third of the industrial organizations surveyed said they prefer to deploy 5G private networks.
However, 5G private networks present significant challenges to manufacturers and their partners. They need to ensure network coverage, connectivity, and stability. Achieving this goal require a full network lifecycle strategy.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Keysight Technologies Acquires Quantum Benchmar, Augmenting Keysight‘s Quantum Portfolio
- Keysight First to Gain GCF Approval of Cases for Validating 5G New Radio mmWave Devices in Standalone Mode
- Keysight‘s O-RAN Test Solutions Enable Xilinx to Accelerate Development of Massive MIMO Radio Reference Design
- Keysight and Transphorm Create Power Supply Reference Design that Lowers Product Costs; Speeds Time to Market
- Keysight Massively Parallel Board Test System Selected by LACROIX in Automotive Printed Circuit Board Manufacturing
- Keysight, TIM and JMA Wireless Join Forces to Showcase O-RAN Technology at Mobile World Congress 2021
- Keysight Delivers New Solution for Benchmarking 5G End-user Quality of Experience in Indoor Environments
- Keysight First to Gain OmniAir Qualified Test Equipment Status, Accelerating C-V2X Device Certification
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































