Silicon Labs Low-Power Wi-Fi Ideal for Energy Efficient IoT Devices
Wi-Fi may not be the first wireless technology you think of when considering a low-power application, but it should be.
The IoT is one of the fastest-growing sectors in the world, with more devices added to the Internet every day. We need access to information and knowledge most efficiently and securely possible and with minimal delay. Consumer electronics, especially wearable devices, are probably the most visible proof of this with more than a billion devices expected to be in use by the end of this year. It's hard to attribute this proliferation to anyone specific protocol. Take a smartwatch, for instance, which might use a Wi-Fi network to sync fitness data, classic Bluetooth to stream audio to earphones, ANT to transmit heart rate sensor data, and Bluetooth Low Energy (LE) to send notifications to a smartphone.
Why Wi-Fi Protocol for IoT Devices
Wi-Fi is a widely deployed protocol with more than 22 billion devices, which means that it's virtually ubiquitous and available in most homes and commercial environments. It has a significantly higher data throughput - almost 10-100x higher than most IoT protocols, which enables audio and video streaming with almost no delay. The high data rates, as well as the range, enable many different applications. Finally, Wi-Fi offers constant cloud connectivity, making gateways unnecessary. With these benefits, Wi-Fi is emerging as an obvious choice for embedded solutions.
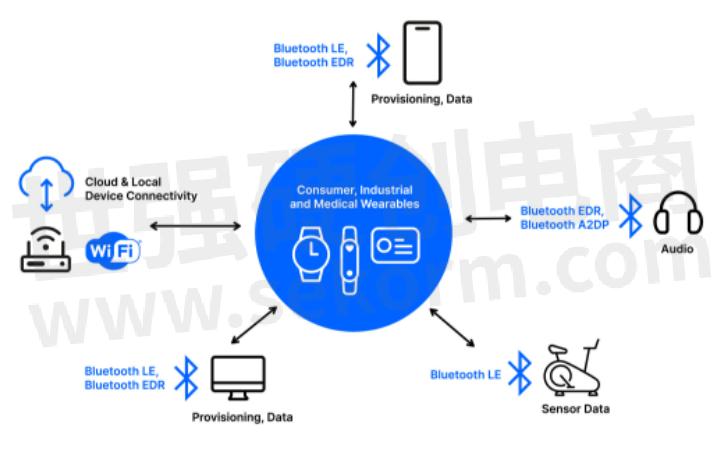
Wi-Fi 4 Versus Wi-Fi 5 Versus Wi-Fi 6 for IoT Devices
Looking at the evolution of the Wi-Fi specification, 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) is better suited for IoT applications than 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5). One reason is that 802.11n is dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) versus 802.11ac which is single-band based on 5 GHz. For embedded applications, the range and better object penetration of 2.4 GHz come in handy compared to the 5 GHz frequency. Also, the cost and power consumption of 802.11ac-based systems is higher due to the higher protocol complexity. While 11ac does provide enhanced throughput, the data rates provided by 802.11n are more than sufficient for most battery-operated IoT applications. 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) is the latest version of the specification, promising a maximum throughput speed of 9.6 Gbps, compared to 3.5 Gbps on Wi-Fi 5 and 600 Mbps on Wi-Fi 4. Wi-Fi 6 was introduced mainly to address the rapid increase in the number of devices on Wi-Fi networks fueled by the growing demand for IoT devices.
Low Power Wi-Fi Design Decisions for Unique IoT Applications
The low power features available in the latest Wi-Fi standards mean that a lot of today’s IoT devices are "always-on" and connected, with extended battery life due to ultra-low power consumption. For example, a Wi-Fi/Bluetooth LE smart-lock application connects to the cloud via Wi-Fi for remote access and provisions the lock onto the Wi-Fi network using Bluetooth LE. Keep in mind that operations like securing cloud connectivity (TLS certificate exchange), network communication (MQTT to communicate with the cloud), and over-the-air (OTA) updates happen in the background further impacting the system's current consumption. By optimizing power consumption, the typical battery life for the smart lock staying in an "always connected" mode is three years for a low congestion environment and two years for a dense and congested wireless environment.
Smaller devices like smartwatches pose additional challenges with space and battery life. Small form factor SiP modules are ideal for sleek designs with a quick time to market. Wearables often require GPS connectivity for location tracking, Wi-Fi for cloud connectivity, Bluetooth A2DP for music streaming, and Bluetooth LE to connect to sensors. All these operations need to be performed in addition to OTA updates while extending the battery life as long as possible on a single charge. Wi-Fi client devices in listening mode take as much power as when they are receiving data. For this reason, the "always-on" feature of Silicon Labs' RS9116 family of SoCs is essential in providing high performance with ultra-low power consumption.
With widespread technology like Wi-Fi gaining traction with IoT devices, standalone or in a multiprotocol mode, it provides the immense potential to transform industries. For a more in-depth look at designing Low-Power Wi-Fi applications, see our whitepaper, “The Future of Wi-Fi in Low-Power IoT Devices."
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Novus Labs‘ test report on 100 routers shows RS9116 Robust low-power Wi-Fi Interoperability
- New Matter Solution from Silicon Labs Unifies the IoT Connectivity Experience
- Silicon Labs Simplifies IoT Development with Simplicity Studio 5
- Silicon Labs Strengthens Isolated Gate Driver Portfolio
- Software Speeds Development of IEEE 1588 System Integration | Silicon Labs
- News | Silicon Labs and Amazon Collaborate on Sidewalk, a New Shared Network for IoT Consumer Devices
- Silicon Labs Expands Isolated Gate Driver Product Family Ideal for Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (EV)
- Silicon Labs and Skyworks reach agreement to sell infrastructure and automotive business
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































