How to Choose Lipo Battery for Medical Device?

Selecting the right lithium polymer (LiPo) battery for medical devices is crucial for ensuring their reliability, efficiency, and safety. Medical devices span a wide range of applications, from wearable fitness trackers and portable diagnostic tools to implantable devices and life-saving equipment like pacemakers and defibrillators. Each application has unique power requirements, and the choice of battery can significantly impact the device's performance and user experience. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the key factors to consider when choosing LiPo batteries for various types of medical devices, ensuring optimal functionality and patient safety.

Fig.1
What types of batteries are primarily used in medical devices?
Medical devices primarily use several types of batteries, including:
●Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Batteries: Known for their high energy density, lightweight, and flexible form factor.
●Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries: Popular for their high energy density and long cycle life.
●Nickel-Metal Hydride (NiMH) Batteries: Used for their stability and safety features.
●Alkaline Batteries: Commonly used in single-use, disposable applications.
●Silver Oxide Batteries: Often used in small devices like hearing aids and pacemakers due to their small size and stable voltage output.
Why do medical devices use LiPo batteries?
LiPo batteries are favored in medical devices for several reasons:
●High Energy Density: They provide a lot of power in a compact size, which is crucial for portable and implantable medical devices.
●Lightweight: Minimizes the overall weight of the device, improving portability and user comfort.
●Flexible Form Factor: Can be molded into various shapes and sizes to fit the design requirements of different medical devices.
●Long Cycle Life: Offers extended operational periods, reducing the need for frequent replacements or recharges.
●Low Self-Discharge Rate: Ensures the battery retains its charge over time, essential for reliability in critical medical applications.

Fig.2
Which medical devices use LiPo batteries?
Here are the types of medical devices that use LiPo batteries, classified from different perspectives such as wearable, portable, implantable, and others:
●Wearable Medical Devices
1. Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers: Used to monitor heart rate, steps, sleep patterns, and other health metrics.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM): For continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels, especially for diabetes patients.
3. Wearable ECG Monitors: To continuously monitor heart activity and detect arrhythmias.
4. Wearable Blood Pressure Monitors: For continuous monitoring of blood pressure levels.
●Portable Medical Devices
1. Portable Oxygen Concentrators: Provide oxygen therapy to patients with respiratory conditions.
2. Portable Ultrasound Devices: Used for diagnostic imaging in remote locations or emergency settings.
3. Insulin Pumps: Deliver continuous insulin to manage diabetes.
4. Portable Ventilators: Provide respiratory support to patients with breathing difficulties.
5. Portable Defibrillators: Used to provide emergency treatment for cardiac arrest.
6. Sleep Apnea Screening: Portable devices used to screen for sleep apnea outside of a hospital setting.
7. Asthma Inhaler: Devices like smart inhalers that monitor usage and provide feedback.
●Implantable Medical Devices
1. Neurostimulators: Provide electrical stimulation to the nervous system for pain management or movement disorders.
2. Cochlear Implants: Provide a sense of sound to individuals with severe hearing loss.
●Diagnostic and Monitoring Devices
1. Hearing Aids: Amplify sound for individuals with hearing impairment.
2. Holter Monitors: Continuously record heart activity over 24-48 hours.
3. Digital Thermometers: Provide accurate body temperature readings.
4. Pulse Oximeters: Measure blood oxygen saturation levels.
5. Medical Light: Devices used for diagnostic purposes, such as examining wounds or during surgical procedures.
●Therapeutic Devices
1. Portable Infusion Pumps: Deliver medications, nutrients, or fluids to patients.
2. TENS Units (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): Provide pain relief through electrical nerve stimulation.
3. Light Therapy Devices: Used for treating skin conditions or mood disorders.
4. Dental Device: Devices used in dental treatments, such as dental drills or dental imaging equipment.
●Emerging and Future Medical Devices
1. Smart Wearable Patches: Flexible patches that monitor vital signs or deliver medication.
2. Advanced Prosthetics: Prosthetic limbs with integrated sensors and actuators for enhanced functionality.
3. Bioelectronic Medicines: Devices that interact with the body's nervous system to treat conditions without drugs.
4. Remote Patient Monitoring Systems: Devices that monitor patients' health metrics and transmit data to healthcare providers.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Fitness trackers?
A wearable device that monitors and tracks fitness-related metrics such as steps taken, distance walked, calories burned, and sometimes heart rate and sleep quality.
●Size and Weight: Fitness trackers need compact and lightweight batteries. Prismatic or pouch LiPo cells are common.
●Capacity: Typically between 100mAh and 200mAh, providing several days of use.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life (300-500 cycles) is important for daily charging.
●Safety: Ensure the battery has protections against overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuits.

Fig.3
How to choose LiPo Batteries for heart rate monitors?
A device that measures and records the electrical activity of the heart to detect irregularities. Often included in wearable fitness trackers or smartwatches to monitor heart rate continuously.
●Capacity: Moderate capacity, around 100mAh to 300mAh, to support continuous monitoring.
●Size and Weight: Compact and lightweight to ensure comfort.
●Voltage: Typically 3.7V.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life (300-500 cycles) for daily use.
●Safety: Suitable for skin contact and certified for wearable use (e.g., ISO 10993).

Fig.4
How to choose LiPo Batteries for continuous glucose monitors
A device that continuously tracks blood glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing real-time data and alerts for individuals with diabetes.
●Size and Weight: Small and lightweight, typically prismatic or pouch cells.
●Capacity: Around 50mAh to 200mAh, sufficient for continuous monitoring.
●Voltage: Stable output, typically 3.7V.
●Safety: Biocompatible and safe materials, with certifications like ISO 10993.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life to support frequent charging.
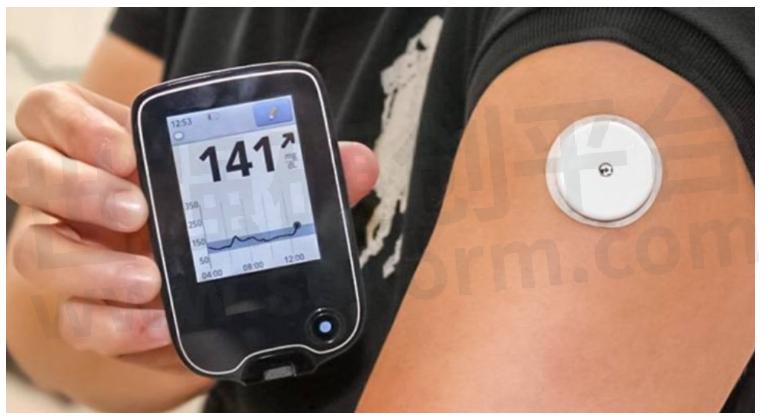
Fig.5
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Blood Pressure Monitor
A device that measures blood pressure non-invasively. Wearable versions can provide continuous monitoring, while traditional models use a cuff that inflates to measure blood pressure at intervals.
●Capacity: Moderate, around 500mAh to 1000mAh, for regular use.
●Size: Compact to fit within the measurement device.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Safety: Certified for medical use, with overcharge and over-discharge protection.
●Recharge Cycles: Long cycle life for frequent recharging.

Fig.6
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Portable Oxygen Concentrators?
A device that extracts oxygen from the surrounding air and delivers it to patients with respiratory conditions, providing a continuous supply of oxygen in a portable form.
●Capacity: These devices typically need batteries with a capacity of 4000mAh to 8000mAh to provide several hours of use. The exact capacity required depends on the power consumption of the concentrator and the desired runtime.
●Voltage: Ensure the battery voltage matches the device’s requirements, often 7.4V (2S configuration) or 11.1V (3S configuration).
●Safety: Look for batteries with certifications such as UL, CE, or IEC 62133. Medical-grade batteries often have additional safety features like thermal cut-offs and pressure relief valves.
●Size and Weight: Consider the physical dimensions and weight of the battery to ensure it fits within the device's design constraints without adding unnecessary bulk.
●Discharge Rate (C-rating): Ensure the battery can handle the high power draw of the concentrator, typically 1C to 2C continuous discharge rate.

Fig.7
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Insulin Pumps?
A small device that delivers continuous insulin therapy through a catheter placed under the skin, helping manage blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes.
●Capacity: High capacity, often 1000mAh to 2000mAh, to ensure reliable operation.
●Size and Weight: Compact to integrate easily into the pump design.
●Voltage: Consistent and stable, typically 3.7V.
●Safety: Certified for medical use, with overcharge and over-discharge protection.
●Recharge Cycles: Long cycle life for daily recharging.

Fig.8
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Ultrasound Device?
A diagnostic tool that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of structures inside the body. Portable versions allow for use in remote or emergency settings.
●Capacity: High capacity, often 2000mAh to 5000mAh, for extended operation.
●Voltage: Ensure it matches the device’s requirements, often 7.4V or higher.
● Safety: Medical-grade certifications and robust safety features.
●Size: Depending on device design, ensure it fits within the housing.
●Discharge Rate: Able to handle high power draw, typically 2C to 5C continuous discharge rate.
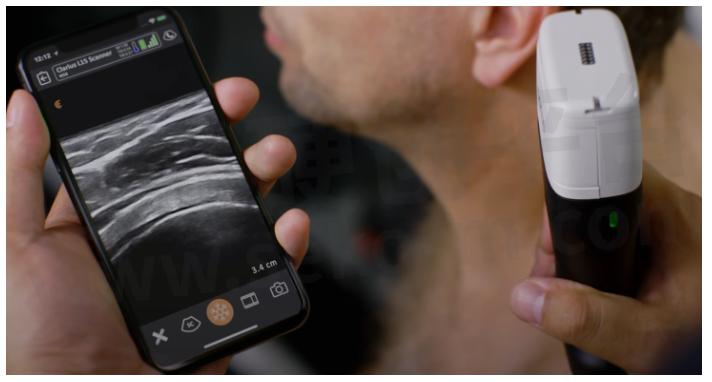
Fig.9
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Sleep Apnea Screening
Devices used to monitor and diagnose sleep apnea by tracking breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other metrics during sleep.
●Capacity: High enough for overnight use, typically 1000mAh to 2000mAh.
●Size: Compact and lightweight for comfortable use.
●Voltage: Consistent and stable, typically 3.7V.
●afety: Non-toxic and safe materials, with certifications like ISO 10993.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life for frequent recharging.

Fig.10
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Portable Ventilators?
Portable ventilators are critical devices for patients who require respiratory support. These devices must be reliable and capable of operating for extended periods without interruption. Choosing the right LiPo batteries for portable ventilators involves considering several key factors:
●Capacity : Ventilators need high-capacity batteries to support continuous operation. Look for batteries with capacities ranging from 2000mAh to 8000mAh or more, depending on the ventilator's power consumption and the desired operational duration.
●Voltage: Ensure the battery voltage matches the ventilator’s specifications, often around 12V (3S configuration) or 14.8V (4S configuration).
●Discharge Rate (C-rating): Ventilators require a moderate discharge rate to ensure stable power delivery. A discharge rate of 5C to 10C is typically sufficient.
●Safety: Safety is paramount in medical devices. Look for batteries with certifications such as UL, CE, or IEC 62133. Ensure they have built-in protections against overcharge, over-discharge, short circuits, and thermal runaway.
●Size and Weight: The battery should be compact and lightweight to maintain the ventilator's portability.

Fig.11
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Portable Defibrillators?
Portable defibrillators, such as Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs), require reliable and powerful batteries to ensure they function effectively in emergency situations. Here’s what to consider:
●Capacity (mAh): Typically, AEDs require batteries with capacities ranging from 2000mAh to 5000mAh to deliver multiple shocks and operate for extended periods.
Voltage: Ensure the battery voltage matches the device’s specifications, usually around 14.8V (4S configuration).
●Discharge Rate (C-rating): AEDs require a high discharge rate to deliver the necessary energy for defibrillation, typically around 20C.
●Safety: Look for batteries with certifications such as UL, CE, or IEC 62133. These batteries should also have built-in protections against overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuits.
●Size and Weight: Ensure the battery fits within the device's design constraints and doesn’t add excessive weight.
●Longevity: Choose batteries with a high cycle life, capable of maintaining performance over several years.

Fig.12
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Asthma Inhaler?
A handheld device that delivers medication directly to the lungs to relieve asthma symptoms. Some smart inhalers track usage and provide feedback.
●Capacity: Sufficient for multiple uses, typically 100mAh to 500mAh.
●Size: Compact and lightweight to fit within the inhaler.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Safety: Non-toxic and safe materials, with protections against overcharge and short circuits.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life for frequent recharges.

Fig.13
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Neurostimulators?
An implanted device that sends electrical signals to specific areas of the nervous system to treat chronic pain, movement disorders, or other neurological conditions.
●Precision: Batteries must deliver consistent power for precise neurostimulation. Low self-discharge and stable voltage are crucial.
●Safety: High safety standards and biocompatibility are a must. Look for batteries with medical-grade certifications.
●Capacity: Adequate capacity to support long-term use, typically 500mAh to 2000mAh.
●Voltage: Stable output, usually around 3.7V.
●Size: Small form factor to fit within the device.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Cochlear Implants?
Cochlear implants require small, reliable batteries to power the device that helps improve hearing:
●Size: Very small and compact, often using coin cell or button cell LiPo batteries.
●Capacity: Typically between 10mAh to 50mAh, sufficient for daily use.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Longevity: High cycle life, as these batteries need to be recharged frequently, commonly rated for 300-500 cycles.
●Safety: Non-toxic, biocompatible, and safe materials, with certifications such as ISO 10993.
●Recharge Speed: Fast charging capabilities to minimize downtime for users.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for OTC Hearing Aids
Over-the-counter devices that amplify sound to help individuals with hearing loss. These are typically less expensive and more accessible than prescription hearing aids.
●Size: Hearing aids require very small, compact batteries. Coin cell or button cell LiPo batteries are commonly used.
●Capacity: Usually ranges from 10mAh to 50mAh, sufficient for a full day of use.
●Voltage: Typically 3.7V.
●Longevity: High cycle life is essential, as these batteries need to endure daily recharges. Look for batteries rated for 300-500 cycles.
●Safety: Non-toxic and safe materials are crucial, along with certifications like ISO 10993 for biocompatibility.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Oxygen Monitor
A device that measures the oxygen saturation level in the blood and pulse rate. Commonly used in both clinical and home settings.
●Capacity: Adequate for extended use, generally 500mAh to 1000mAh.
●Size: Compact to ensure the monitor remains portable.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life for frequent recharging.
●Safety: Certified for medical use with protections against overcharge and short circuits.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Medical Light?
Devices used to provide illumination for diagnostic examinations, surgical procedures, or therapeutic purposes.
●Capacity: High to support extended use, often 2000mAh to 5000mAh.
●Voltage: Ensure it matches the light’s requirements, often 7.4V or higher.
●afety: Medical-grade certifications and robust safety features.
●Size: Depending on device design, ensure it fits within the housing.
●Discharge Rate: Able to handle high power draw, typically 2C to 5C continuous discharge rate.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Holter Monitors?
Holter monitors are used for continuous heart rate monitoring over 24-48 hours or longer, requiring reliable and long-lasting batteries:
●Capacity: Typically between 500mAh to 1000mAh to support continuous monitoring.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Size: Compact to ensure the monitor remains portable and comfortable for the patient.
●Longevity: High cycle life to support frequent recharges.
●Safety: Certified for medical use with protections against overcharge, over-discharge, and short circuits.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Digital Thermometers?
Digital thermometers require small, reliable batteries for accurate temperature measurement:
●Capacity: Typically very small, around 100mAh to 200mAh.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Size: Compact to fit within the thermometer housing.
●Safety: Safe and non-toxic materials, with certifications like UL and CE.
●Longevity: Moderate cycle life, as these devices are not used continuously.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Bioelectronic Medicines
Devices that use electrical stimulation to modulate the body's nervous system to treat diseases and conditions without drugs.
●Precision: Consistent and stable power delivery is crucial. Low self-discharge and stable voltage are necessary.
●Safety: High safety standards and biocompatibility, with certifications like ISO 10993.
●Capacity: Moderate to high, around 500mAh to 2000mAh, depending on usage.
●Voltage: Stable output, typically 3.7V.
●Size: Small form factor to fit within the device.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Smart Wearable Patches
Flexible patches that adhere to the skin and monitor various health metrics, such as heart rate, glucose levels, or temperature, often with integrated sensors and wireless communication.
●Size and Weight: Ultra-compact and lightweight, typically prismatic or pouch cells.
●Capacity: Sufficient for continuous monitoring, around 50mAh to 200mAh.
● Voltage: Typically 3.7V.
●Safety: Certified for skin contact with biocompatible materials (e.g., ISO 10993).
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life to support frequent recharging.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Advanced Prosthetics
Prosthetic limbs with advanced functionality, including integrated sensors, actuators, and sometimes neural interfaces, providing improved movement and control for amputees.
1. Capacity: High to support advanced functions, often 1000mAh to 3000mAh.
2. Size and Weight: Compact and lightweight to integrate seamlessly.
3. Voltage: Stable and consistent, typically 3.7V.
4. Safety: Biocompatible and safe materials, with certifications like ISO 10993.
5. Recharge Cycles: Long cycle life for daily recharging.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Remote Patient monitors
Systems that use various devices to monitor patients' health metrics remotely, transmitting data to healthcare providers for continuous care and management.
●Capacity: High for continuous monitoring, typically 1000mAh to 3000mAh.
●Size: Compact and lightweight for portability.
●Voltage: Stable output, typically 3.7V.
●Safety: Certified for medical use, with robust safety features.
●Recharge Cycles: Long cycle life for frequent recharging.
How to choose LiPo Batteries for Dental Device
Various tools and equipment used in dental care and treatments, including drills, imaging devices, and orthodontic appliances.
●Capacity: Moderate to high, around 500mAh to 2000mAh, for consistent use.
●Size: Compact to fit within the device.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Safety: Certified for medical use, with overcharge and over-discharge protection.
●Recharge Cycles: High cycle life for frequent recharging.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Portable Infusion Pumps
Infusion pumps require reliable and long-lasting batteries to ensure continuous medication delivery:
●Capacity: Typically between 1000mAh to 3000mAh to ensure extended operation.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Size and Weight: Compact and lightweight to integrate easily into the pump design.
●Safety: Certified for medical use, with robust safety features like overcharge and short circuit protection.
●Longevity: High cycle life to support frequent recharges.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for TENS Units
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) units require reliable batteries to deliver pain relief therapy:
●Capacity: Typically between 500mAh to 1000mAh to support multiple therapy sessions.
●Voltage: Standard 3.7V.
●Size and Weight: Compact and lightweight for portability.
●Safety: Certified for medical use with protections against overcharge and short circuits.
●Longevity: High cycle life to support frequent recharges.
How to Choose LiPo Batteries for Light Therapy Devices
Light therapy devices require powerful batteries to support prolonged use:
●Capacity: Typically between 2000mAh to 5000mAh to ensure extended operation.
●Voltage: Ensure it matches the device’s requirements, often 7.4V or higher.
●Discharge Rate (C-rating): Able to handle high power draw, typically around 2C to 5C continuous discharge rate.
●Safety: Medical-grade certifications and robust safety features.
●Size and Weight: Depending on device design, ensure it fits within the housing and doesn’t add unnecessary weight.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the selection of flexible LiPo batteries for medical devices requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including capacity, voltage, size, weight, safety, and longevity. Each type of medical device has specific requirements that must be met to ensure reliable operation, patient safety, and user comfort. By understanding these requirements and choosing the appropriate Lipo Battery specifications, manufacturers can enhance the performance and reliability of their medical devices, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes. Whether for wearable fitness trackers, portable diagnostic tools, or critical implantable devices, the right LiPo battery choice is essential for advancing medical technology and providing better healthcare solutions.
FAQ Are lipo batteries safe for medical device applications?
LiPo batteries can be safe for medical device applications if they are specifically designed and certified for such use.
How long do medical device batteries typically last?
Battery lifespan varies depending on usage and type but generally lasts months to years. Lipo batteries typically last 2 to 5 years or around 300 to 500 charge cycles.
Can medical device batteries be recharged?
Some medical device batteries are rechargeable, while others are disposable and cannot be recharged. Lipo and NiMH Batteries can be rechargeable. alkaline or lithium primary cells cannot be recharged.
What certifications are needed for medical device lipo batteries?
When selecting LiPo batteries for medical devices, it is essential to ensure they meet specific certification requirements to guarantee safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards. Here are the key certifications required:
●ISO 13485: This certification indicates that the batteries are manufactured in accordance with the international standards for quality management systems specific to the medical device industry.
●IEC 62133: This standard pertains to the safety requirements for portable sealed secondary cells, and it is crucial for batteries used in medical devices to meet these criteria.
●UL 1642: This certification ensures the batteries have passed rigorous testing for safety and performance, including assessments for potential hazards like overheating, short-circuiting, and overcharging.
●CE Mark: For batteries used in the European market, the CE mark is essential as it signifies compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
●UN 38.3: This certification is crucial for batteries that will be transported by air, sea, or land, ensuring they have passed tests for altitude simulation, thermal tests, vibration, shock, external short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge.
What safety certifications are needed for the transportation of medical device batteries?
When transporting LiPo batteries for medical devices, ensuring they have the appropriate safety certifications is vital to prevent hazards during transit. Here are the necessary safety certifications for transportation:
●UN 38.3: This certification is mandatory for lithium batteries transported by air, sea, or land. It includes tests for altitude simulation, thermal tests, vibration, shock, external short circuit, impact, overcharge, and forced discharge.
●IATA DGR (Dangerous Goods Regulations): Batteries must comply with the International Air Transport Association’s regulations for the safe transportation of dangerous goods by air.
●IMDG Code (International Maritime Dangerous Goods): For batteries transported by sea, compliance with the International Maritime Organization's regulations for dangerous goods is required.
●49 CFR (Code of Federal Regulations): In the United States, batteries must meet the Department of Transportation's hazardous materials regulations for safe transportation.
●ADR (European Agreement Concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road): For road transport in Europe, batteries must comply with the ADR regulations to ensure safe and secure transportation.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- What is a Smart Ring Battery and The Manufacturing Process?
- Grepow Rechargeable Li-lon Button Cells Solutions for High-tech Applications
- 12V UPS Battery FAQs
- Can Lithium Batteries and Lead Acid Batteries be Used Together?
- What Is LiFePO4 Battery and Why Use It?
- Grepow Battery will exhibit at 2022 Summer Asia Smart Wearable Exhibition
- Grepow covers a wide range of shaped batteries to maximize the use of product space, perfectly adapted to small portable electronic products
- Thin Film Lithium-ion Battery Vs Lithium-ion Battery: What’s the Difference?
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































