Material Choices: An Important Criterion in Selecting High-Frequency Capacitors

Radio frequency (RF) and microwave applications involve the transmission and receipt of high-frequency electromagnetic signals. RF refers to alternating current (AC) signals at 3 kHz to 300 GHz, and microwave refers to a higher range, closer to 300 MHz to 300 GHz. Capacitance, and by extension impedance, varies with frequency, so Capacitors play a variety of critical roles in these RF and microwave circuits. With many options for configuration, they function in energy storage and voltage regulation, DC blocking, impedance matching, filtering and more.

Understanding the capacitance achievable in a given area is an important factor in choosing capacitors for your application. This is ultimately determined by the type of dielectric material that can meet your application requirements for space and capacitance, see Figure 1.
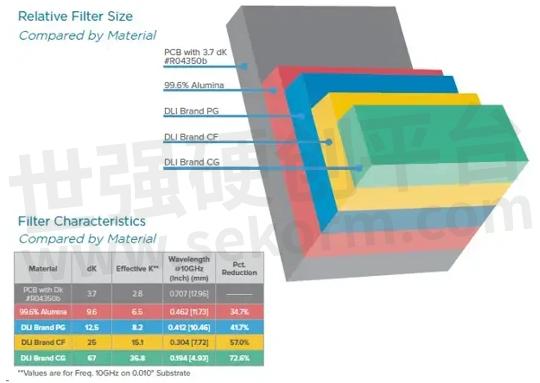
Figure 1: Comparing dielectric materials by relative filter size and characteristics
For AC coupling/DC blocking applications where capacitance tolerance and temperature stability requirements are more forgiving, consider Class II dielectrics. In applications with tighter tolerances, like LC filters, Class I dielectrics are a better choice because of their excellent stability and low-loss characteristics.
A majority of Knowles Precision Devices’ single-layer capacitors (SLCs) are 0.02” x 0.02” (20 mil sq) to 0.03” x 0.03” (30 mil sq). That said, we’ve seen growing demand to lower case sizes to 0.010” x 0.010” (10 mil sq). To meet this demand, Knowles Precision Devices has a range of offerings from a dielectric constant (K) of 9 through 45000. See Figure 2 for Knowles Precision Devices Class I and Class II dielectric materials and relevant specifications.
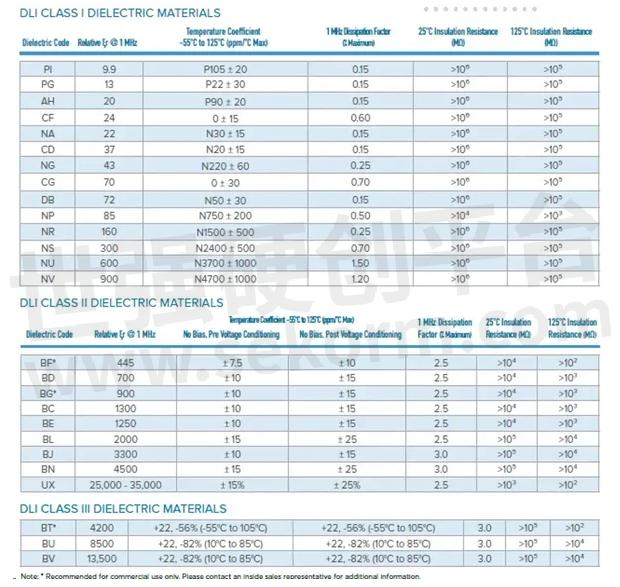
Figure 2: Knowles Precision Devices Class I, II and III dielectric material offerings and key specifications to consider
There are additional factors at play when selecting components for high-frequency, high-performance applications. Substrate properties, like surface finish, and fabrication processes, like metallization, impact the accuracy of line width and gap width. Both of these parameters impact overall circuit performance.
When looking for high-performance microwave substrates, focus on:
Low loss tangent to reduce dielectric loss
Uniform, isotropic dielectric constant to minimize inconsistencies like impedance changes within the circuit
Batch-to-batch repeatability in manufacturing
Smooth surface finish to minimize conductor ohmic losses
High thermal conductivity for power electronics circuits
Thermal expansion that complies with component and package requirements
Knowles Precision Devices offers custom dielectrics and standard High-Frequency Capacitors that meet and exceed these parameters.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- What are Flying Capacitors?
- Capacitors Support Radar MMIC Amplifiers via Bypassing
- Capacitors for External Defibrillators
- How Gold Capacitors Work?
- Nippon Chemi-Con GOB, MXB and HSF Sereis Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors with an Upper Category Temperature of 150℃
- Supercapacitor Manufacturer SRT Explain How Solid Capacitors Work
- Supercapacitor Manufacturers SRT Take You Through the Main Parameters of Capacitors
- Knowles Achieves a Benchmark for Excellence: MIL-PRF-55681-Qualified Capacitors for Mission-Critical Defense Applications
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































