Choose Servo without Getting Lost: How to Choose the Right Servo According to the Specifications!


Servo is a type of position (Angle) servo driver, suitable for control systems that require constant changes in Angle and can be maintained. Often used in a variety of model aircraft, car models, and toy drones. At first, it was often used in various model airplanes, car models, and toys. It is characterized by simple control, low cost, small volume, and large torque; With the progress of servo production technology, it is now applied in aerospace, large drones, robots, medical treatment, industrial automation and other fields. At the same time, there are more and more types of servos. In the face of the different needs of different industries, how to efficiently and quickly choose their own appropriate servo has become a more concerning problem. Next, take Desheng's specifications as an example to sort out several technical indicators of servo for you:

Servo specifications mainly have the following aspects: torque, working Angle, speed, communication protocol, working voltage, housing and gear material, size, motor type, accessories, and so on. When we do the selection of servo, we should consider the above aspects comprehensively.
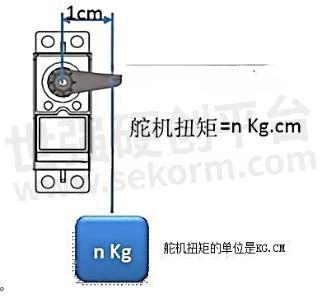
torque
The unit of servo torque is kgf.cm, which is a torque unit. It can be understood as the weight of the object that the servo can drive at the horizontal distance of 1CM from the servo axis on the steering wheel. It is usually divided into rated torque and blocked torque. Rated torque refers to the torque that the steering engine can continue to output under a normal working environment, and the selection is generally made with reference to the rated torque of the servo. Locked-in torque refers to the maximum torque applied by the steering gear when the output shaft is prevented from rotating. The greater the locked-in torque, the stronger the servo's ability to withstand external loads.
NM conversion: 1NM=9.8/kgf.cm
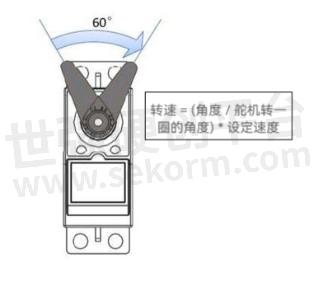
Speed:
Rotation speed by the servo without load 60°; Angle required time to measure, mainly affected by motor type, voltage, gearbox reduction ratio, and other factors.
Control Angle (position sensor type) :
Control Angle: conventional 180° , 360° Angle controllable, N*360 multi-circle Angle control
Position sensor: 0-320° Potentiometer is available inside, 360° Angle and multi-turn air magnetic encoders are many, but also Hall.
Potentiometer, because it is contact, wear, used for life requirements, are not too high, long life accuracy requirements are not high working conditions.
The magnetic encoder is non-contact, used for long life, stable performance, long life and high precision requirements.
Voltage:
Servo speed, torque data, and other performance parameters and voltage related, in the 6V and 7.4V two test voltage these two parameters have a relatively large difference. For example DS-H003:

The operating voltage of the servo has a significant effect on the performance. In general, for small servo due to working equipment reasons, the working voltage is usually 4.8V, 6V, and 7.4V, while some industrial equipment on the servo is above 7.4V, such as 12V, and 24V servo. Within the voltage range of the steering gear, a higher voltage can increase the speed and torque of the motor. When selecting the servo, it is also necessary to consider whether the locked-rotor current of the servo is within the range of the main control board, and too high a current will cause the main control board to overheat and burn.
Motor Type:
As the power source of the servo motor, it is also roughly divided into four kinds of motors such as iron core brush, hollow cup, and brushless motor, motor performance is directly related to the torque and speed of the servo. Among them, the brushless motor is the most, the speed is higher, the torque is larger, and the large torque servo is generally brushless; The Core motor with cost-effective advantage in the market to occupy a place; The hollow cup is favored in the small application market with the advantages of small size and fast heat dissipation, and the performance is between the two.
Housing and gear material:
The material here mainly refers to the servo housing and gearbox.
Servo housing is roughly divided into plastic housing, semi-aluminum frame, and full metal housing. The plastic material is lighter in weight and lower in cost, the metal material is good in heat dissipation, and beautiful, and the metal shell is also better in water resistance.
Gears are divided into plastic gears and metal gears. Plastic teeth have low sound and low cost, while metal teeth have better load capacity, impact resistance, and life.
The servo of plastic gear may break teeth in the case of gridlock, and the servo of metal gear may be damaged by overheating of the motor. Therefore, the choice of material is not an absolute tendency, the key is to use the servo within the design specifications.
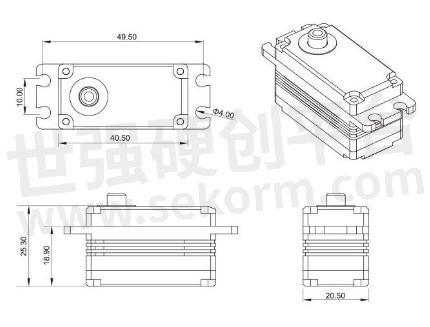
Size, weight:
Size and weight are two key parameters in servo selection. The size directly affects the installation space of the servo, while the weight affects the overall stability and carrying capacity of the equipment. When selecting the servo, it should be reasonably evaluated according to the specific needs and installation conditions of the equipment size and weight to ensure the servo can fit the equipment and meet performance requirements.
Communication protocol:
The servo needs to communicate with the control card or other devices in practical applications, so it is equally important to choose the servo that matches the device communication. At present, there are four common communication protocols used by servo on the market, which are: (1) PWM (potentiometer lead can do position feedback, easy to be interfered with, not recommended); ②TTL (mostly used in STEAM education, robotic arm programming, slightly slower than other bus read back), ③RS485 (RS422, etc.), ④CAN bus, ⑤PLC control. In addition to PWM, the rest are bus types, which can achieve series control, real-time feedback, and adjustment
Accessory:
It is also important to choose the right accessories for the servo, for example, the servo rocker arm, the steering wheel, etc. The selection of these accessories should be matched according to the specific requirements of the servo use. Manufacturers will buy servo at the same time as the standard accessories package, but whether it is plastic or metal, manufacturers are supporting customized. At the same time, considering the compatibility and tightness, the plastic link opening mold can allow the servo manufacturer to provide inserts; If the metal connector can also provide the output tooth drawings, the adaptation will be better。

In summary, the selection of a servo involves many aspects of parameters, including torque, working Angle, speed, communication protocol, working voltage, housing and gear material, size, motor type, accessories, and so on. In practical applications, we need to comprehensively consider these parameters according to the needs of the equipment and operating conditions to select the most suitable servo. In addition, when purchasing the servo, it is also necessary to pay attention to the technical parameters and performance indicators provided by the manufacturer to ensure that the purchase meets the requirements of the servo.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- What Is Servo? How Does the Servo Work?
- Nidec Develops AC Servo Motor Equipped with Zignear® , the Location Detection Technology that Accommodates 17-bit Resolution, for the Industrial Robot Market
- How Is the Servo Controlled Through PWM?
- Nidec Launches a Lineup of VR Series Servo Motor Reducers for Food Machinery, Achieving a Torque of up to 80% of Standard Models
- DSPOWER Durable 20KG Class Semi-aluminum Frame Metal Tooth Servo DS-S020B Has a Maximum Torque of 28kgf.cm
- Robot Servo: Key Elements Analysis and Selection Guide
- Nidec Launches New Models of FLEXWAVE Precision Control Reducers,Facilitating Servo Motor Installation
- Application of DSpower Servo in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV)
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































