Coherent SmartWeld+ Processing Head Fills the Gaps in Production Welding

Production automation expert teamtechnik supplies everything from manual through fully automatic turnkey systems for manufacturing, assembly, and testing. Their expertise spans a huge range of technologies, including part handling, various testing methods, and joining processes, mainly for the e-mobility industry. In 2019, they were asked to develop a production welding system by a manufacturer of battery packs for handheld power tools.

In particular, teamtechnik was tasked with providing automated solutions for welding 11 different joints. These included joining a variety of materials together. Because they didn’t have extensive in-house expertise in laser welding, and so many processes had to be developed in short order, they reached out to COHERENT Labs to assist them.
A SMARTER WAY TO WELD
The Coherent team was supplied with material samples. A series of tests readily demonstrated that all these processes could be accomplished with the Coherent SmartWeld+ processing head, coupled with a 1kW, single-mode fiber laser (the HighLight FL1000CSM).
SmartWeld+ is a specialized welding tool that incorporates an advanced form of beam shaping, including a wide variety of oscillation patterns. It also enables precise control of delivered laser energy during the weld process. Together this allows the width, depth, and penetration profile of the weld seam to be carefully managed. It’s particularly useful for joining heat-sensitive materials and dissimilar material combinations, such as copper to aluminum or steel. Also, it can weld highly reflective or volatile materials with less spatter, porosity, and cracking.
DIFFICULT MATERIALS
SmartWeld+ even enables the processing of “difficult” materials – that is, those that aren’t traditionally compatible with laser welding. Some of the materials utilized in the battery pack construction fell into this category.
For example, one weld requires joining a 0.5 mm thick piece of zinc-coated copper to a 1.0 mm thickness of nickel-coated copper. The low melting point of zinc has presented problems for laser welding in the past. In particular, it bubbles chaotically when brought to the temperature necessary to melt copper. This results in voids and porosity in the finished weld seam, as well as a substantial amount of spatter.
This part required welds on both ends. One end was flat, and the other end had a 90° bend. These conditions were different enough that two separate sets of parameters had to be developed to optimize each weld. Plus, there is a plastic piece embedded in the part that must not be heated during welding.
The ability to adjust the exact shape of the weld using SmartWeld+ was very useful here. It allowed the creation of a joint that was large enough to provide the required level of electrical connection and mechanical strength without straying too close to the plastic part. While similar weld paths are used on each side of the part, the directions they are applied are different. The development teams in teamtechnik Poland and Coherent also found that for one of the welds, optimum weld results were obtained with a small gap between the parts.
For both welds, a key part of the solution was dynamic power modulation. This provides the ability to stabilize the melt pool during welding and eliminate porosity. It also substantially reduces spatter.
HANDLING PROCESS VARIABILITY
Another of the welds involved joining two 0.3 mm thick pieces of SIGMACLAD® together. SIGMACLAD
is a composite material specifically designed for making electrical
connections in Li-Ion batteries in packs. It’s a five-layer sandwich
consisting of Ni|stainless steel|Cu|stainless steel|Ni. This combination
delivers more desirable properties than any individual metal.
Specifically, copper provides excellent electrical and thermal
conductivity (for heat dissipation), while the stainless steel layers
make the material easier to weld and also increase weld joint strength.
The outer nickel layers facilitate soldering and lend good corrosion
resistance.
Because SIGMACLAD is specifically designed for
compatibility with laser welding, neither the teamtechnik nor Coherent
development teams expected that this join would represent much of a
challenge. But, in practice, they found that material thickness
variations, individual layer thickness variations, and low overall part
dimensional tolerances created process deviations and inconsistent fit-up. Testing determined that fixturing would be necessary to keep any gap
between the two parts to less than 0.05 mm to achieve a 100%
success rate for the welds.
The overall weld in this case is 1 mm x 2.5 mm. The focused laser
beam is much smaller than this, so the SmartWeld+ traces the beam back
and forth several times while stepping slightly in the perpendicular
direction between each scan to cover the entire area. Furthermore,
testing showed that it was necessary to modulate the laser while moving,
otherwise there was excessive spatter at the ends of the scan.
Some of the processes changed even after the equipment was installed and commissioned in the end user’s factory. The Coherent applications group continued to provide support to respond to this.
For example, in one weld 0.3 mm thick SIGMACLAD is joined to 1.0 mm thick nickel-coated copper. The problem here didn’t arise until after the equipment had been installed and operated successfully by the end user for two years. Then the materials supplier changed their formulation and also introduced issues with the cleanliness of the copper. This resulted in a substantial amount of spatter using the process recipe which they had originally employed without difficulties.
The flexibility of the SmartWeld+ proved particularly valuable in this case. In particular, the ability
to easily vary the weld parameters through software control without
making any changes to the hardware of fixturing. A new cycle of testing
at Coherent established that implementing laser power modulation in this
process would solve the problem.
PARTNERING FOR SUCCESS
Working with the Coherent development team allowed teamtechnik to concentrate on what they know best – namely automation. “We needed a partner to get all these laser welding processes developed within the time and cost constraints we had from our customer,” notes Maciej Zaborowski, Welding Technology Specialist, teamtechnik POLAND. “In particular we wanted to find someone who has the expertise and facilities to test the materials and determine if they could all be laser welded, and then develop specific process recipes that would work in production.”
“Coherent delivered on all these points. Plus, our cooperation with them didn’t end after this initial process development. They’ve continued supporting us as changes in materials created production variances in processes that had been working well up to then. There was no other laser vendor we could find who would take on this level of process responsibility.”


Figure 1. Cross section and top view of the 0.5 mm zinc-coated copper to 1.0 mm nickel-coated copper weld.


Figure 2. Cross section and top view of the 3mm SIGMACLAD to 3mm SIGMACLAD weld. 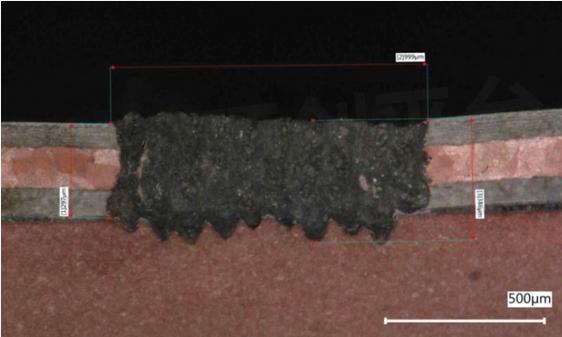

Figure 3. Cross section and top view of the 3mm SIGMACLAD to 1.0 mm nickel-coated copper welds.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Coherent Introduces New Ph20 Smartweld+ Laser Processing Heads for Precision Welding at High Speeds in EV Applications
- Coherent ARM Fiber Laser and SmartWeld+ Surpass Traditional Remote Welding Systems is Reinventing Laser Processing for EVs
- Coherent Showcased Award-Winning 100G and 400G Coherent Transceivers at OFC 2023
- SMART Modular Technologies to Present at SNIA Persistent Memory + Computational Storage Summit
- Coherent Demonstrated Next-generation Transceiver Technology for Digital Coherent Optics in Ultracompact Pluggable form Factors for Disaggregated Systems at ECOC 2023
- SMART Modular Announces the SMART Kestral PCIe Optane Memory Add-in-Card to Enable Memory Expansion and Acceleration
- Coherent Introduces I-Temp Micro-Pump Lasers for Extended Temperature Operation in Broadband Optical Access Networks
- SMART‘s DDR4 Modules Range From 32GB To 4GB, 20% Lower Overall Power Vs. DDR3
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































