BGA SSD: Powerful NVMe Performance in a Tiny Package

Solid-state drives (SSDs) have come a long way from being hard disk drive (HDD) replacements. Today, SSDs meet the storage-hungry needs of smart factories, autonomous vehicles, intelligent buildings, mobile applications, and more. As the network of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) keeps expanding, embedded systems keep downsizing while data storage requirements keep expanding. This has become a constant challenge for NAND flash-based storage device manufacturers. From early-generation SSDs that were the size of HDDs, current SSDs are tinier but are expected to hold more data, perform reliably in extreme operating conditions, last longer, and deliver the best total cost of ownership.

Powerful NVMe Performance in a Tiny Package
The NVMe protocol has revolutionized the storage industry by delivering performance 4X-6X the speed of SATA’s 6 Gb/s by using the PCI Express (PCIe) interface. Initially available as M.2 modules, PCIe NVMe SSDs were small, slim, and powerful, offering unprecedented speeds and the lowest latency for industrial applications.
ATP brings NVMe level performance to a tiny form factor: the N700 Series PCIe Gen3 x4 NVMe M.2 Type 1620 heatsink ball-grid array solid-state drive (HSBGA SSD). These SSDs come with the high-speed PCIe 3.0 interface x4 lanes and NVMe protocol to deliver up to 32 Gb/s bandwidth at 8 Gb/s per lane, while dimensions of just 16 (L) x 20 (W) x 1.6 (H) mm, the M.2 Type 1620 form factor, and 291-ball packaging take up minimal space within tightly confined systems.
The HSBGA in M.2 Type 1620 form factor is designed to be soldered down, making it resistant against vibrations and shocks. For customers who prefer a removable and field-replaceable design, ATP can accommodate the HSBGA onto an M.2 2230 module with the same firmware and NAND configuration. Both variants are suitable for thin and light systems in embedded, industrial and automotive applications.
N700 Series SSDs are built with 3D triple-level cell (TLC) configured as pseudo-single-level cell (pSLC) NAND flash. By storing only one bit per cell, they increase the reliability and endurance of the NAND flash memory, while benefiting from the lower cost compared with native SLC, due to the higher cell density.
The Thermal Challenge
An increase in speed does come with big benefits, especially for applications requiring real-time data computation and analytics. It also comes with heating challenges, especially because of the HSBGA’s small size, and because embedded systems typically have little or no airflow and are often installed in constrained spaces.
Overheating can cause damage to or even failure of the storage device, thus posing risks to the integrity of the stored data.
A common approach to the overheating challenge is thermal throttling, which helps cool the device by slowing down performance. When activated, traditional thermal throttling mechanisms will abruptly cause performance downgrades, thus compromising the device’s sustained performance.
ATP’s Customizable Thermal Management Solutions
Recognizing that effective thermal dissipation is critical to achieving sustained performance, ATP has come up with its own-built Thermal Management Solutions that are customizable depending on customers’ needs and considering other factors, such as the system environment, mechanical design, and performance criteria.
ATP’s Thermal Management Solution combines both hardware and firmware to address the unique thermal challenges and needs of varied applications.
ATP works closely with the customers and system developers to make sure that the NVMe HSBGA SSD delivers higher sustained performance even while operating at high workloads and extremely hot temperatures.
· The ATP Optimized Thermal Throttling firmware will maintain the “Steady State” condition to avoid huge performance drops that will adversely impact the system, thus optimizing best performance for application requests and enhancing overall sustained performance.
· Heatsink on Top, which effectively transfers heat to cool the device and keep the performance at optimal levels

Figure 1. The heatsink consists of layers of different metals that offer excellent thermal and electrical conductivity to effectively dissipate heat.
Enhanced Sustained Performance
With ATP’s Thermal Management Solutions, the N700 Series SSDs improved sustained performance 2X-3X the previous levels.
The following graphs show sustained performance under the ATP Optimized Thermal Throttling mechanism.
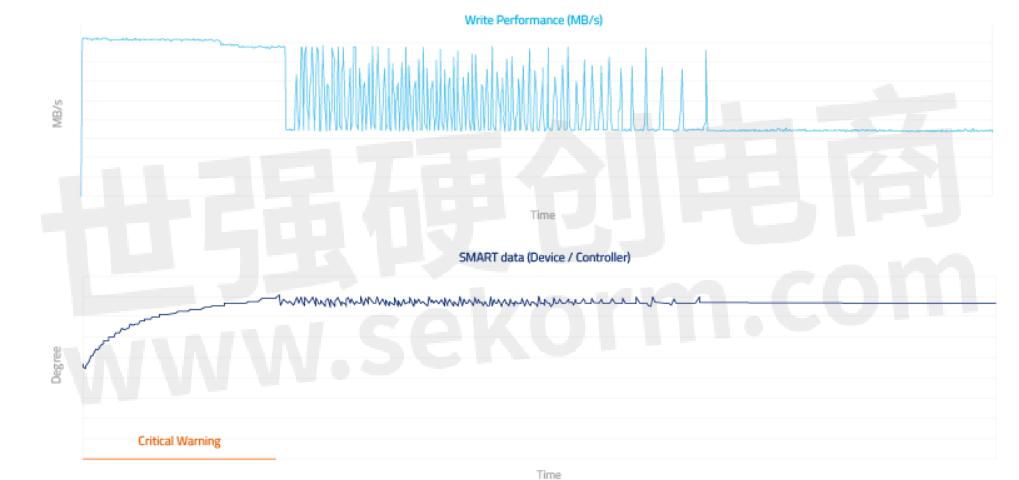
IOMETER Sequential Write | 80 GB pSLC| Environment Temperature: 75°C, no Air Flow
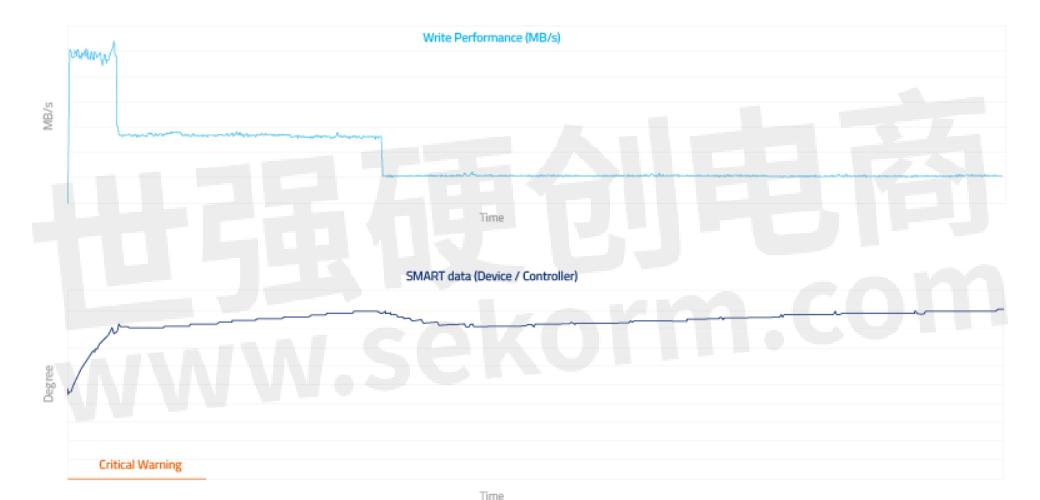
IOMETER Sequential Write | 160 GB pSLC | Environment Temperature: 75°C, no Air Flow
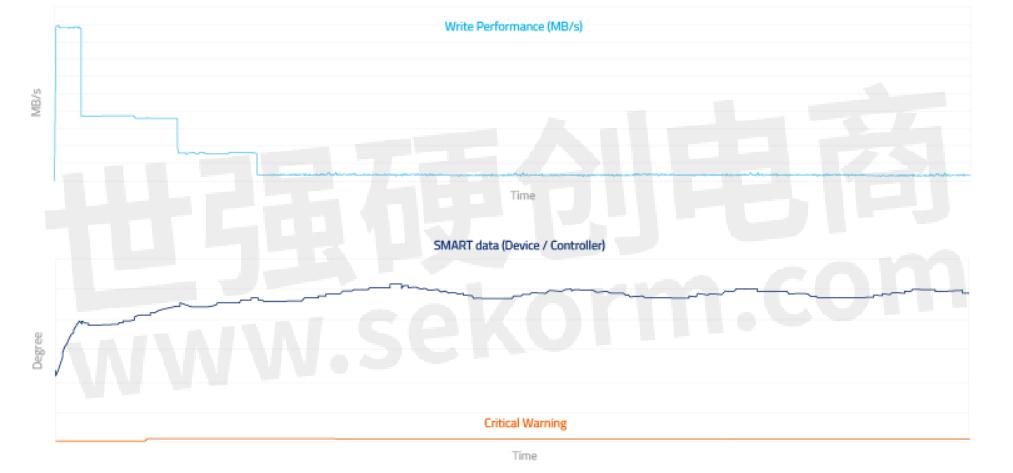
IOMETER Sequential Write | 160 GB pSLC | Environment Temperature: 55°C, with Air Flow
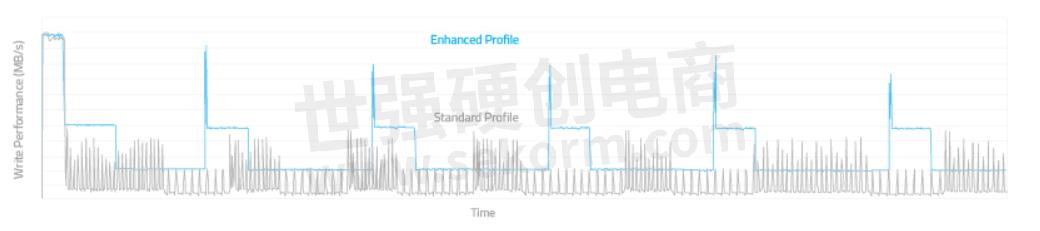
The following graphs compare the N700 Series configured with pSLC (Enhanced Profile) vs. TLC SSDs with SLC cache (Standard Profile), showing 2X-3X improvements in sustained performance after the implementation of ATP’s Thermal Management Solutions.
IOMETER Sequential Write | 40 GB pSLC @ 25°C | 120 GB TLC with SLC Cache @ 25°C
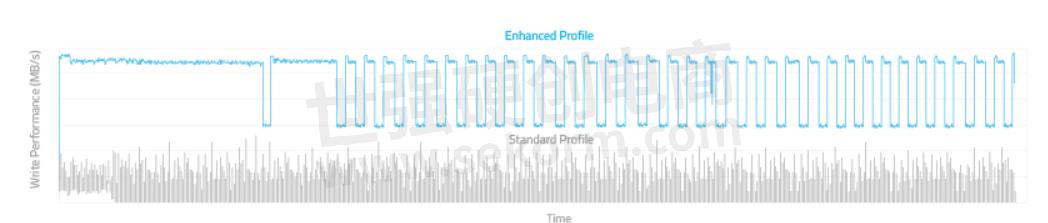
IOMETER Sequential Write | 160 GB pSLC @ 25°C | 480 GB TLC with SLC Cache @ 25°C
N700 Series Key Features
·pSLC Mode. Configured to store only one bit per cell to increase endurance and reliability, offering 2X-3X sustained performance.
·Stable Performance. The ATP Optimized Thermal Throttling firmware (FW) will maintain the “Steady State” condition to avoid huge performance drops that will adversely impact the system, thus optimizing best performance for application requests and enhancing overall sustained performance.
·Optimized Power Consumption. Consuming low power at only 5 mW during Power State 4 (Sleep Mode), the ATP NVMe HSBGA SSDs deliver huge power savings.
·DRAM-Less Configuration. Host Memory Buffer (HMB) support helps these DRAM-less SSDs to improve performance by obtaining DRAM resources as cache, thus overcoming the limited memory capacity within the storage and optimizing I/O performance without requiring the SSD to bring up its own DRAM
·Vibration-resistant Storage. ATP N700 Series SSDs in M.2 Type 1620 is soldered down, making them vibration-resistant and able to withstand rigorous shaking.
·Better Thermal Dissipation. The heatsink effectively transfers heat to cool the device and keep the performance at optimal levels.
Optional Security Features
·HW Write Protect
·HW Quick Erase
·HW Secure Erase
·SW Data Sanitization (AFSSI-5020)
·AES-256 Encryption
·TCG Opal 2.0
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.


























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































