The Difference between SIM Card and SD Card

SIM card is the
abbreviation of subscriber identification module, also known as a user
identification card or smart card. GSM digital mobile phone must be
installed with this card before it can be used. The size of Sim can be
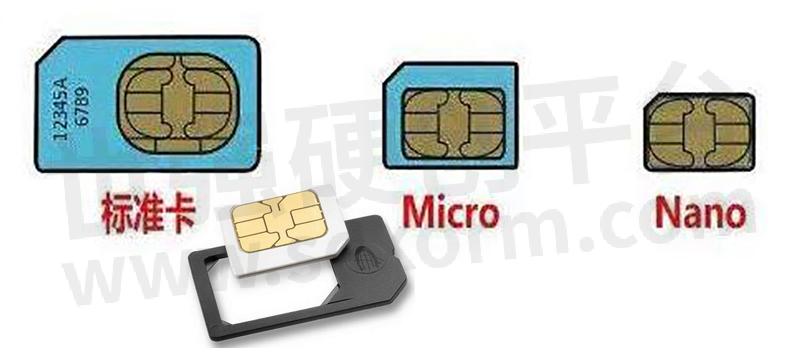
divided into three types: standard card 25 × 15 × 0.8mm; micro SIM card
12x15 × 0.8mm; nano SIM card 12.3 × 8.8 × 0.7mm; nano SIM card 12.3 ×
8.8 × 0.7mm; SIM card size: 25 × 15 × 0.8mm; micro SIM card: 12x15 ×
0.8mm; nano Sim card: 12.3 × 8.8 × 0.7mm.
In
general, the IC chip of a SIM card has 128KB storage capacity, which can
store the following information: 1000 sets of telephone numbers and
their corresponding names and characters, 40 groups of short messages,
more than 5 groups of newly dialed numbers, and 4-digit SIM card
password (PIN).
There
are more than 16K, 32K, 64K, 128K, 512k, and 1m SIM cards on the market,
as well as professional SIM cards that can provide multimedia services
and non-contact services. The capacity can reach M-level.
The SD card was jointly launched by Panasonic, Toshiba, and SanDisk, and
was released in August 1999. The data transmission and physical
specification of the SD card are developed from MMC. The size of the SD card is
similar to that of the MMC card. The size is 32 x 24 x 2.1 mm. The length
and width of the MMC card are the same, but 0.7mm thicker than the MMC
card to accommodate a larger storage unit. SD and MMC cards are
compatible upward. MMC cards can be accessed by new SD devices.
Compatibility depends on application software, but SD cards cannot be
accessed by MMC devices.
SD capacity has 8MB, 16MB, 32MB, 64MB, 128MB, 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, and 2GB
The capacity of SDHC is 2GB, 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, and 32GB
The capacity of SDXC is 32GB, 48GB, 64GB, 128GB, 256GB, 512GB, 1TB and 2TB
The
speed classification method of SD card in sd2.0 specification is: the
speed of the ordinary card and the high-speed card is defined as class 2, class
4, class 6, and class 10. Before the release of the class 10 card, there were
cards of class 11 and class 13 for a while, but this standard was not
finally agreed upon by SDA.
Sd3.01
specification is called ultra high-speed card, and the rate is defined
as uhs-i and uhs-ii. As of the second quarter of 2013, only uhs-i cards
had been listed. Uhs-ii was released in the fourth quarter of 2012, but
in terms of the speed of technology development before 2014, uhs-i is
fully enough to last 2014 or even longer. The speed level of the uhs-i card
is divided into uhs-class0 and uhs-class1. The class of uhs-i is
different from that of sd2.0. There is no clear class 0 card, which
literally means that the card cannot reach class 1. Maybe the old class
standards in the future will be classified as class 0. Class 1 represents
the maximum read rate of 104MB/s, while the class in sd2.0 standard
represents the minimum write speed range.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.

































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































