Learn the Basics of Signal Generator Accuracy

Jumping into the world of Signal Generators for the first time can be a daunting journey. There are lots of technical considerations, and it is not always obvious which ones are the most important to focus on. In this article, Keysight will provide guidance on the things you need to be aware of when selecting an RF signal generator.
What is a Signal Generator?
Signal generators provide precise, highly stable, and customizable test signals for a variety of components and system test applications that emulate real-world scenarios. The outputs can be anything from a simple continuous wave to more complex modulated digital signals. Signal generators are an important part of product development because they enable you to apply signal impairments to test your product in various conditions within and beyond design limitations.
What Affects Signal Generator Accuracy?
Amplitude Accuracy
Amplitude accuracy compares the proximity of the signal generator's output to the desired amplitude set by a user. If we use the example of frequency sweeping to test filters and power amplifiers, choosing a signal generator with a tighter amplitude frequency specification provides a more uniform output across a frequency range. Figure 1 illustrates the flatness of a signal generator when determining the amplitude accuracy across a group of frequencies.
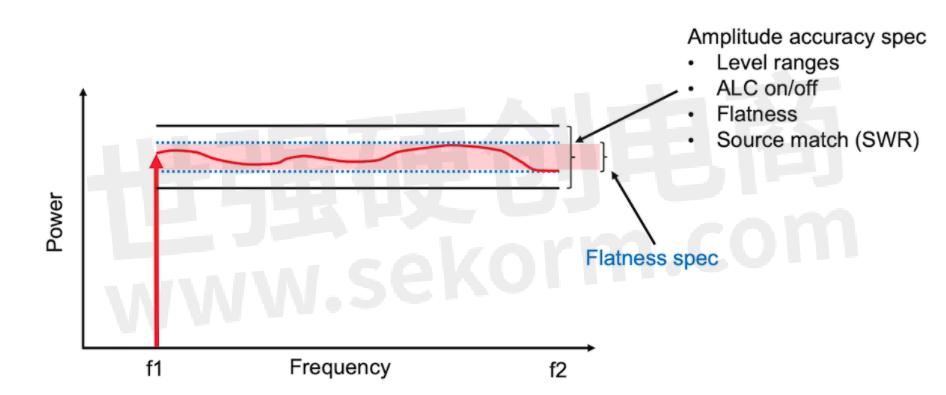
Figure 1. Amplitude accuracy of a source across the frequency
Frequency Accuracy
Two key factors for understanding the accuracy of a generated frequency are the stability of the reference oscillator and the time between source calibrations. The time between calibrations is also known as the aging effect. Frequency accuracy is vital to RF applications especially where bands have data that are closer together. For example, in wireless communications, it is important to understand how well a receiver can process a signal while rejecting the signal from an adjacent channel. Poor frequency accuracy will cause the signals to be too close or too far and give a misleading indication of the performance of the device under test (DUT).
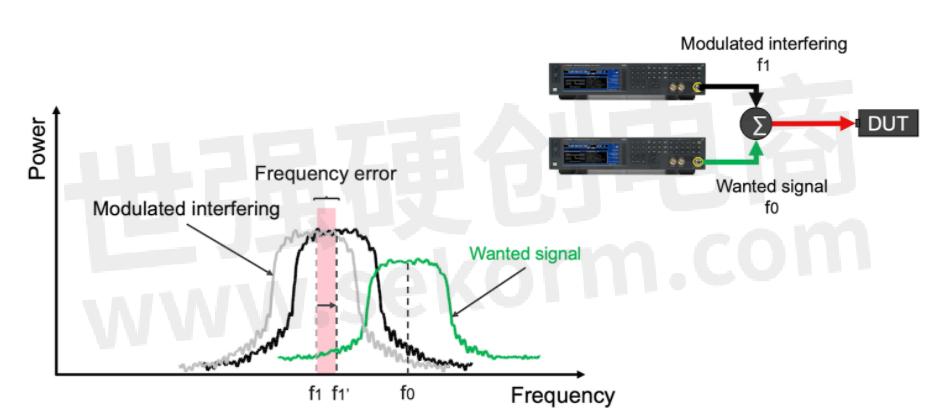
Figure 2. Error difference between the desired signal and generated signal
Spectral Purity
Every signal generator has an unwanted amplitude and phase fluctuations on a signal that naturally occurs. Regardless of a source's signal stability, choosing a signal generator that has better spectral accuracy compared to the system requirements will prevent you from measuring the signal generator performance versus the DUT. Spectral purity is characterized by evaluating harmonics, sub-harmonics, spurs, and phase noise. In datasheets, it's common to see the spectral purity represented as the single side band (SSB) phase noise.
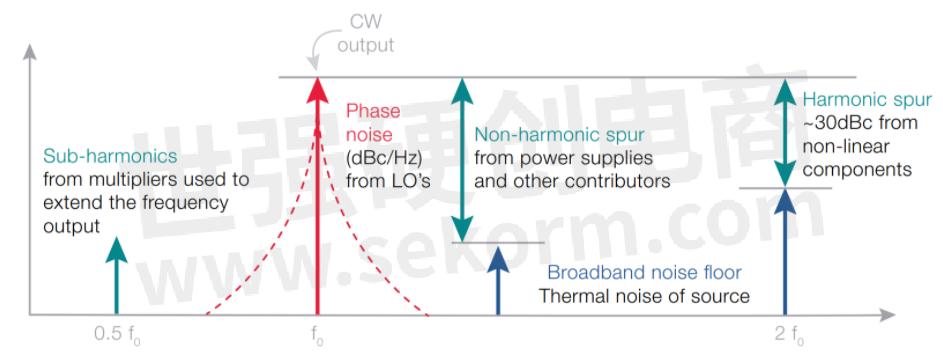
Figure 3. Various non-ideal spectral components
EVM Measurement
Error vector magnitude (EVM) is the vector difference between the ideal reference signal and the measured signal at a given time, as depicted in Figure 4. This is commonly used to define the performance of a digital radio transmitter or receiver. Signal generators designed with smaller EVM percentages enable you to design and test systems to reach higher data capacity, better power efficiency and increase wideband signal power.
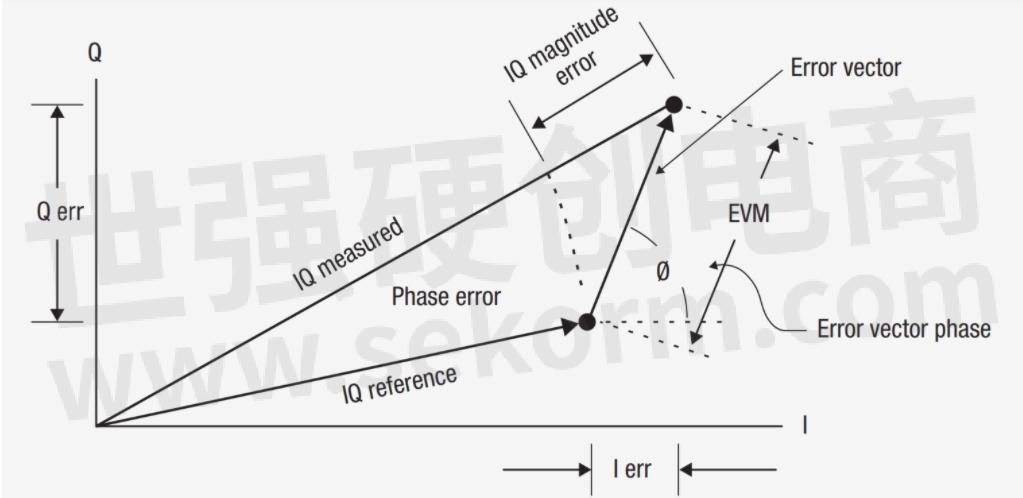
Figure 4. EVM is the difference between the actual measured signal and the ideal reference signal
The impact of distortion on Performance
Spectral regrowth refers to the distortion generated by amplitude and phase shifts in digital modulations. Spectral regrowth spreads outside the main channel and adjacent channel power ratio (ACPR) measurements enable examination of this characteristic. Similar to spectral purity, it's important to choose a signal generator with a superior distortion test margin that won't mask the performance of the DUT.
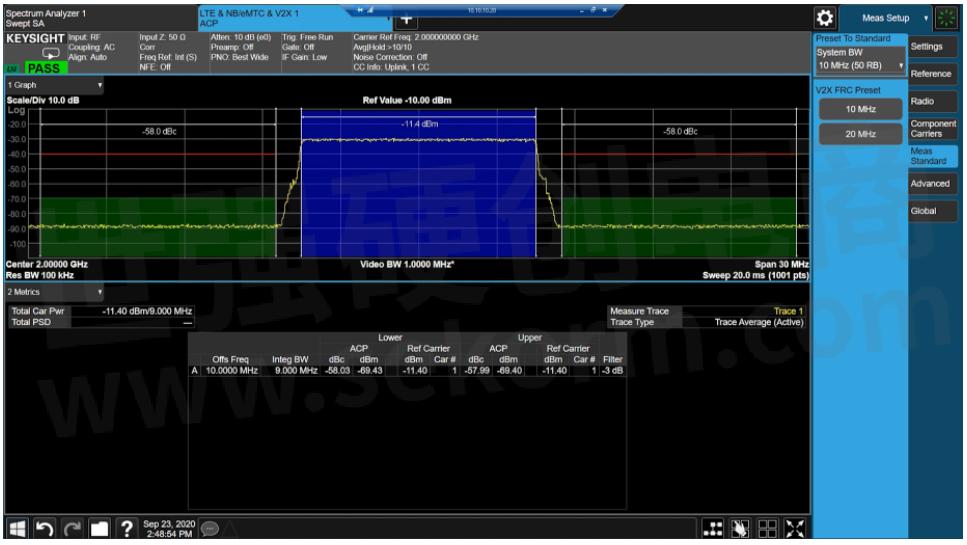
Figure 5. Example of an ACPR measurement
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- The Principle and Use of the Signal Generator
- How to Choose a Signal Generator?
- How to Calculate the Frequency of the Signal Generator?
- The Application Scenarios of Signal Generator
- What Is the Role of Signal Generator in Our Daily Life?
- What Is the Difference Between Microwave Signal Generator and Radio Frequency Signal Generator?
- Keysight Launches Next-Generation Vector Signal Generator N5186A for Dense Wideband Multichannel Applications
- Renesas DSP Solution on Renesas Lab on the Cloud, Input Analog Signals Directly From A Signal Generator To The Rx231 Microcontroller Evaluation Board
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































