How Temperature Affects Data Retention for SSDs

How Does High Temperature Affect Data Retention?
Flash wear in solid state drives (SSDs) is commonly attributed to usage or workload and endurance parameters are often expressed in program/erase (P/E) cycles. Another important, yet often overlooked, factor in SSD endurance is operating temperature. While continuously operating at very high temperatures, the SSD can degrade quickly. In a study held a few years ago, researchers found that "temperature has the most effect on data integrity" and "drives that ran hotter tended to fail the fastest" (Source: Digitaltrends). In settings where there could only be a handful of devices operating simultaneously for a number of hours at most, this heat issue may not be a big concern; but in environments like server farms where hundreds or thousands of devices are running at high speed and maximum performance 24/7, the temperature could go high enough to affect data retention. How can the integrity of data written on the flash drive be guaranteed at high operating or storage temperatures?
High-Temp Scenarios Affecting Data Retention
Prior to deployment, the SSD could lie dormant on a hot shelf for extended periods of time, causing concern that data or programs loaded before shipping will be lost. Since it is easier for electrons to enter or escape in hot temperatures and more difficult to enter or escape in cold temperatures it is best to store unused SSDs at low temperatures.
SSDs retain data by trapping and keeping electrons in the floating gate. Each cycle of electrons going in (programming) and out (erasing) wears out the tunnel oxide. While in use, SSDs subjected to high temperatures due to large workloads and poor thermal management can adversely impact data retention. Over time, when the tunnel oxide weakens, hot temperatures can cause electrons to leak out, resulting in higher bit errors. If there are too many bit errors, uncorrectable errors occur.
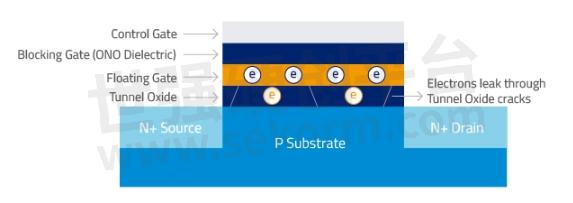
Figure 1. As flash wears out over time, extremely hot temperatures can cause electrons to leak out from the tunnel oxide.
Similarly, SSDs that have been in active use for several years and then stored in high temperatures over long periods of time will have data retention issues.
The JESD218B.01 standard, released by the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association, provides parameters for standardized endurance ratings, including retention requirements at certain temperatures. "This standard is based on use scenario where SSDs are actively used for some time, during which the SSDs are written to their endurance ratings, followed by a power-down time period in which data must be retained." (Source: JESD218B.01. ©JEDEC Solid State Technology Association. 2016. For endurance workload definitions of Client and Enterprise Class SSDs, please refer to JEDEC JESD219A.)
Client-Class SSDs typically used in a 40℃ environment actively for 8-hour periods, must be able to retain data for 1 year in a temperature rating of 30℃ after it is powered off.
Enterprise-Class SSDs typically operating at 55℃ for 24 hours a day should able to retain data for 3 months at 40℃ after it is powered off.
ATP Solutions for Better Endurance and Data Retention
ATP's industrial temperature-rated flash storage products have the ability to perform reliably within a wide temperature range of ‐40℃ to 85℃ and have higher endurance ratings surpassing typical endurance levels of other flash technologies.
Meticulous Validation and Characterization. Stringent quality screening and characterization at IC level and package design validation ensure the reliability of the new die. Complete module functionality tests are performed at the module level, while a 100% Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) during the pilot run ensures proven reliability at the mass production stage. RDT includes built-in self-test (BIST), wide temperature testing, and complete drive test including firmware, user, and spare areas.
Thermal Sensors and Dynamic Thermal Throttling. Embedded SSD modules are designed for high-speed, superior performance in compact systems with space limitations. Slim and pint-sized yet power-packed with features and capabilities, embedded SSDs could be prone to thermal issues especially when operating under high workloads. ATP's industrial-grade embedded SSDs are engineered for the toughest tasks under the most severe conditions.
To ensure outstanding performance and extended reliability in networking, enterprise, data center, and other industrial applications, these rugged SSDs (select models) feature temperature sensors to detect the temperature of the device and the controller. If temperatures reach threshold levels, the Dynamic Thermal Throttling mechanism is activated to prevent the SSD from overheating, automatically adjusting SSD performance to cool it down.
The ATP Dynamic Thermal Throttling mechanism smartly reduces heat without dramatic declines in performance, ensuring that the SSD continues to perform at optimal levels.
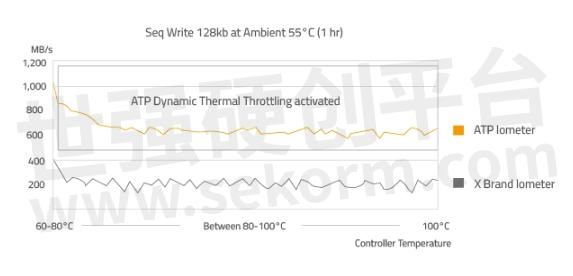
Figure 2. Even when ATP Dynamic Thermal Throttling is activated, ATP's 1 TB NVMe SSD performs two to three times better than other brands at its full strength. This clearly shows that there is no compromise in performance, unlike other solutions that drastically lower performance to reduce heat.
Long Reliability Ratings. ATP's industrial flash storage products are built to perform reliably over long periods of time. Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) ratings of 5 million or 2 million hours (depending on the model) at 25℃ translate to many years of dependable use. All products are designed, screened, tested, and validated according to the strictest standards, from component to product level at ATP's own manufacturing and validation facilities.
Conclusion
As more and more organizations increasingly adopt SSDs as the storage of choice, they also seek more cost-effective ways to balance performance and cost. Many have turned to flash technologies that are capable of higher densities but often face performance, reliability, and endurance challenges and are typically unable to handle extreme temperatures.
ATP industrial SSDs are built to endure long years of dependable use and retain data even under tough operating conditions, workloads, and temperatures. For detailed information on ATP's industrial temperature solutions, visit the ATP website or contact an ATP Representative or Distributor in your area.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.

























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































