SMBJ5347B Voltage Regulator Diode: Comprehensive Analysis of Technical Features and Thermal Design

In the broad field of semiconductor devices, voltage regulator diodes have always been a focal point for engineers due to their unique operating characteristics and wide range of applications. Today, we will delve into the features of the SMBJ5347B, a voltage regulator diode that stands out among its peers with its 10V regulation voltage, 5W power rating, and 5µA reverse current.
1. Technical Specifications Overview
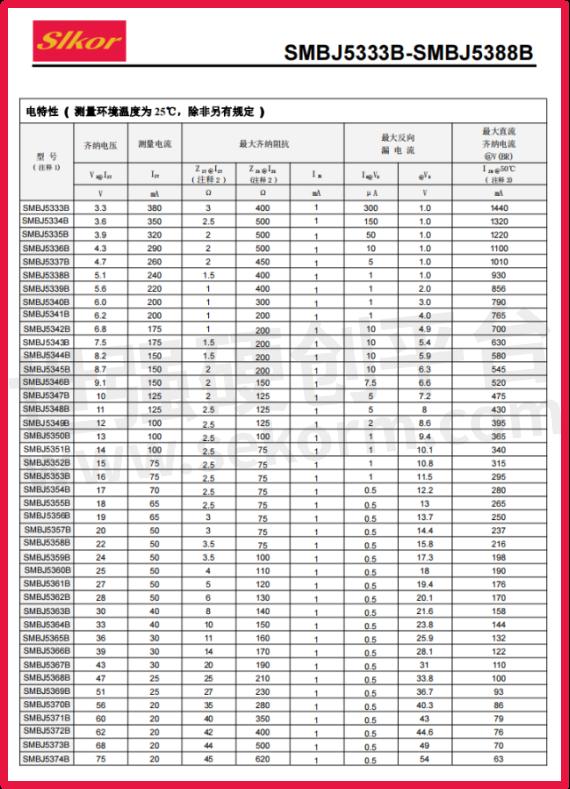
The core parameters of the SMBJ5347B voltage regulator diode include its regulation voltage, power rating, and reverse current. Firstly, its nominal regulation voltage is 10V, meaning that under normal operating conditions, this diode can maintain a stable voltage around 10V, providing a steady voltage environment for the circuit. Secondly, with a power rating of 5W, it can handle relatively high current and power loads, making it suitable for various high-power applications. Lastly, its reverse current of 5µA, a low reverse current characteristic, helps reduce unnecessary power loss and improve overall circuit efficiency.
SLKOR voltage regulator diode SMBJ5348B specification
2. Potential Applications
Due to its exceptional performance, the SMBJ5347B finds extensive applications across multiple fields. In power management circuits, it can be used as a voltage regulation component to ensure the stability of the output voltage and protect subsequent circuits from voltage fluctuations. Additionally, in automotive electronics, industrial control, and consumer electronics, the SMBJ5347B plays a crucial role in providing stable and reliable operating voltages for various electronic devices.
Slkor Voltage Regulator Diode SMBJ5348B specification
3. Design Considerations
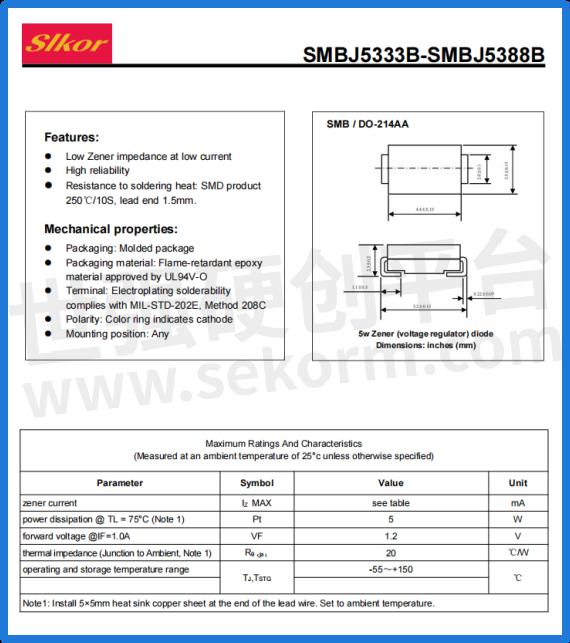
When designing circuits with the SMBJ5347B, engineers need to consider several key factors. Firstly, thermal design is critical, as the device has a high power rating and requires effective heat dissipation to prevent overheating. Secondly, circuit protection should be appropriately designed to handle potential overcurrent and overvoltage scenarios. Finally, selecting and matching components is essential to ensure the SMBJ5347B works harmoniously with other circuit elements to achieve optimal overall performance.
Slkor Voltage Regulator Diode SMBJ5348B specification
4. Thermal Management Principles
The SMBJ5347B generates heat during operation, and if this heat is not effectively dissipated, it can lead to increased device temperature, which may result in reduced performance or even damage. Therefore, the core of thermal management is to efficiently transfer the heat generated by the device to the surrounding environment through effective conduction, convection, and radiation, keeping the device within its normal operating temperature range.
5. Thermal Material Selection
- High Thermal Conductivity Materials: Use materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper or aluminum, for heat sinks or thermal interface materials, to quickly transfer heat from the device to the cooling structure.
- Low Thermal Resistance Materials: Employ thermal pads or thermal grease with low thermal resistance between the device and the cooling structure to reduce thermal resistance in the heat transfer process and improve cooling efficiency.
6. Thermal Structure Design
- Increase Heat Dissipation Area: Design large-area heat sinks or fins to increase the surface area of the cooling structure, thereby enhancing the heat exchange efficiency with the surrounding environment.
- Optimize Airflow Design: When possible, integrate the overall airflow design of the equipment to allow smooth airflow over the cooling structure, improving convective cooling effectiveness.
- Heat Pipe Technology: For high power density or specialized applications, consider using heat pipes to achieve efficient heat transfer through the phase-change process of the working fluid inside the heat pipe.
7. Evaluating Thermal Performance
- Temperature Testing: Under actual operating conditions, use infrared thermometers or thermocouples to measure the temperature of the SMBJ5347B and its cooling structure, ensuring the device temperature does not exceed its maximum allowable operating temperature.
- Thermal Resistance Calculation: Perform theoretical calculations or use simulation software to determine the thermal resistance between the device and the cooling structure, assessing the effectiveness of the thermal design.
- Long-Term Stability Testing: Conduct long-term stability tests under simulated real-world conditions on circuits with the SMBJ5347B to observe temperature trends and performance stability of the device.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- SMBJ5350B Zener Diode: The Perfect Combination of High Performance and Reliability
- SMBJ5355B: The 18V Voltage Regulator Pioneer with High Efficiency
- The Application and Value of SMBJ5361B Zener Diodes in the New Energy Vehicle Sector
- The Exceptional Application of SMBJ5363B Voltage Regulator Diodes in Smart Home Devices
- SMBJ5352B Zener Diode: Unveiling Its Key Role in High-Performance Circuits
- SMBJ5360B Zener Diode with a Nominal Zener Voltage of 25V and Power Rating of 5W
- SMBJ5348B Zener Diode: Exceptional Performance, Industry‘s New Favorite
- SMBJ5349B Zener Diode Provides Effective Lightning Protection for Electronic Devices through Its Fast Response Characteristics and Ability to Absorb Over-Voltage
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































