Zener Diode BZT52B4V7: Characteristics, Applications and Market Competitiveness

Zener diodes play a crucial role in the electronics industry, particularly in circuits requiring stable voltage outputs. Today, we delve into the BZT52B4V7 Zener diode, analyzing its key parameters, operating principles, application scenarios, and market advantages.

SLKOR Voltage Regulator Diode BZT52B4V7 product photo
Interpreting Key Parameters
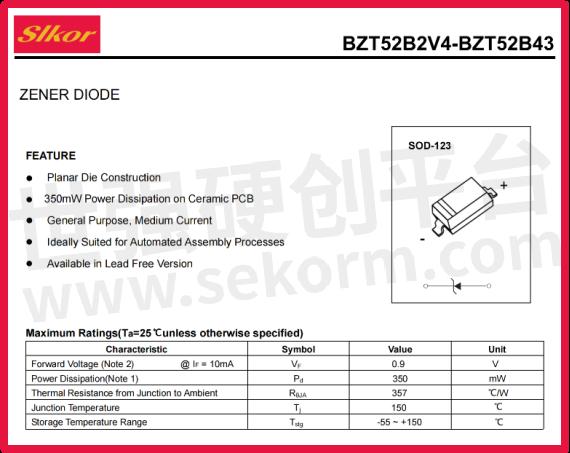
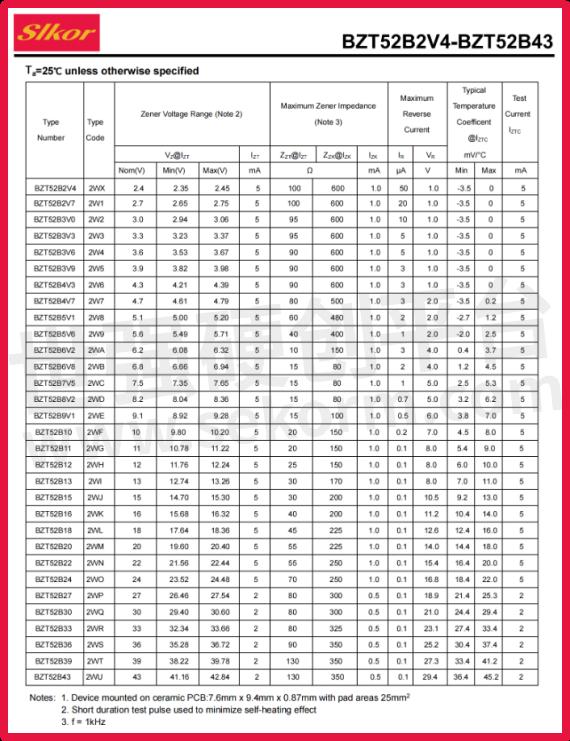
The nominal voltage of the BZT52B4V7 is 4.7V, with a precise voltage range tightly controlled between 4.61V to 4.79V. This exacting voltage range enables the diode to provide stable voltage outputs across various electronic devices, ensuring the circuits operate reliably.
Furthermore, the diode boasts an accuracy of ±5%, meaning its actual voltage deviation in applications will not exceed 5% of the nominal value, thereby guaranteeing circuit stability and reliability.
Slkor Voltage Regulator Diode BZT52B4V7 specification
In terms of power, the BZT52B4V7 is rated at 350mW, a moderate power rating that allows it to function effectively in a variety of electronic devices without excessive energy consumption or inability to meet circuit requirements.
Additionally, the reverse current (Ir) of the diode is specified at 3μA. This low reverse current characteristic aids in reducing power consumption and enhancing overall circuit efficiency.
Parameters of Slkor Voltage Regulator Diode BZT52B4V7
Operating Principles and Typical Applications
The operation of a Zener diode primarily hinges on its reverse breakdown characteristics. When a reverse voltage threshold is reached, the diode conducts, maintaining a stable voltage output. The BZT52B4V7 utilizes this principle to deliver a stable 4.7V voltage in circuits.
Typical applications of the BZT52B4V7 include power supply circuits, protection circuits, and serving as a reference voltage source. In power supply circuits, it ensures voltage stability; in protection circuits, it safeguards other circuit components from overvoltage damage; additionally, it serves as a precise voltage reference for other circuits.
Market Positioning and Competitive Edge
The BZT52B4V7 holds a strong competitive position in the market due to its precise voltage regulation, moderate power rating, and low reverse current characteristics. Compared to similar products, its advantages lie in high accuracy and stability, meeting the demands of various precision electronic devices.
However, engineers must still consider specific application scenarios and requirements when selecting Zener diodes. For instance, high-power or special environment applications may necessitate alternative types of Zener diodes or additional protective measures.
Differential Applications in Analog and Digital Circuits
Zener diodes, as semiconductor devices providing stable voltage, find extensive application in electronic engineering. However, their use varies notably between analog and digital circuits due to differing operational principles and design objectives. Below, we explore the specific applications and differences of Zener diodes in these two circuit types.
Applications in Analog Circuits
In analog circuits, Zener diodes are primarily used to provide stable reference voltages or act as protective components.
●Reference Voltage Source: Zener diodes offer highly stable voltage outputs, making them ideal as reference voltage sources in analog circuits. For example, in amplifier circuits, a Zener diode can serve as a baseline voltage to ensure accurate amplifier outputs.
●Protection Component: Zener diodes can also function as overvoltage protection components. When the circuit voltage exceeds the Zener diode's breakdown voltage, it conducts, diverting excessive voltage to ground and protecting other circuit elements from damage.
Applications in Digital Circuits
In digital circuits, Zener diodes are primarily used to ensure stable logic levels.
●Stable Logic Levels: In digital logic circuits, Zener diodes ensure the stability of logic levels. Since digital signals typically operate at high or low levels, Zener diodes provide a clear threshold voltage to ensure accurate signal recognition.
●Noise Immunity: Digital circuits are susceptible to various forms of noise interference. Zener diodes provide some degree of noise suppression, ensuring stable transmission of digital signals.
Reasons for Differences
The distinct applications of Zener diodes in analog and digital circuits stem from the differing operational principles and design objectives of these two circuit types. Analog circuits focus on continuous signal variation, requiring stable reference voltages and overvoltage protection to ensure signal accuracy and circuit safety. On the other hand, digital circuits deal with discrete signal states, necessitating stable logic levels and noise immunity to ensure reliable signal transmission.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- In-depth Analysis of the Performance and Applications of the Zener Diode BZT52B16
- BZT52B24 Voltage Regulator Diode: The Ultimate Choice for Stability and Performance
- BZT52B30 Zener Diode: Integration of Technical Details and Superior Performance
- Application of Zener Diode BZT52B9V1 in Green Energy Systems
- In-depth Analysis of Zener Diode BZT52B12: Technical Specifications and Applications
- BZT52B5V1 Voltage Regulator Diode: Outstanding Performance Sets a New Industry Standard
- BZT52B2V4 Zener Diode: A Precision Voltage Regulation Choice
- The BZT52B4V3 Zener Diode with The Range of Stability from 4.21V to 4.39V and The Precision Factor of ±5% Accuracy
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































