Must-Know Basic Facts about Digital Isolators

Electrical isolation is a crucial concept in the design of electrical systems. Through the isolation of the high and low voltage systems, the following important functions can be achieved:
1. Make the high and low voltage systems independent of each other and improve the anti-interference capability of the low voltage system;
2. Ensure safe interaction between the high and low voltage systems so that the systems can work safely;
3. Protect users' personal safety by avoiding electric shock from the high voltage.
In this Technical Sharing, the basics of electrical isolation will be introduced in detail, including: the definition and importance of electrical isolation, the classification and definition of isolation levels, and the standards and specifications for isolator certification.
Definition and Importance of Electrical Isolation
Electrical isolation uses isolators to prevent destructive electrical signals from being transmitted between high/low voltage subsystems, while allowing safe electrical signals required for system operation to interact between high/low voltage systems. Three system interaction scenarios are discussed below:
1. When two low voltage systems interact, electrical signals can be freely transmitted between the two systems. In this state, we usually consider the systems to be working safely.
2. When high/low voltage systems interact directly without isolators, due to the high potential difference between the high voltage system and the low voltage system, the high voltage system may transmit destructive electrical signals to the low voltage system, which will cause the low voltage system to malfunction and even cause permanent damage to the low voltage system. This will not only affect the functional safety of the systems, but also endanger personal safety and lead to major safety accidents.
3. After using an isolator for electrical isolation between the high and low voltage systems, destructive electrical signals are blocked by the isolator. Safe electrical signals required for normal system operation interact between the high and low voltage systems, ensuring the functional safety of the systems.
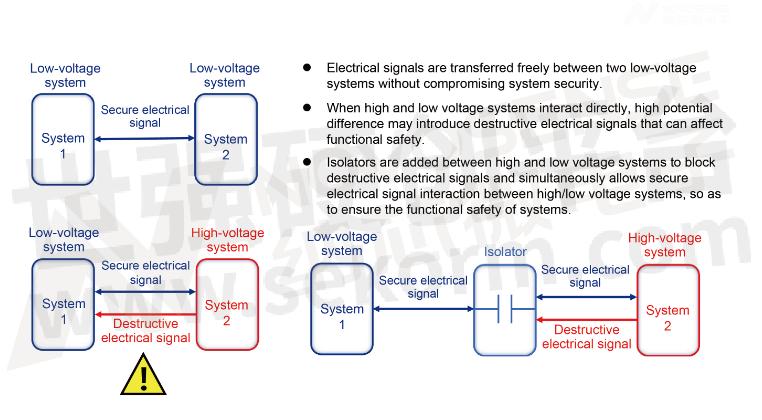
Definition of Electrical Isolation
Classification and Definition of Isolation Levels
Based on different isolation performance, electrical isolation is divided into different isolation levels. Functional isolation, basic isolation, dual isolation, and reinforced isolation are among typical isolation levels:
1. Functional isolation can only achieve the isolation necessary for normal device operation and does not have the function of electric shock protection, such as the PCB materials on the circuit boards.
2. Basic isolation only provides single-stage isolation and can achieve isolation while the insulation layer is intact. But once the insulation layer fails, the system will be at risk of electric shock. Under normal circumstances, the isolation voltage that basic isolators can isolate is around 3kV, and there are a few basic isolators whose isolation voltage can reach 5kV.
3. Dual isolation adds a layer of isolation on the basis of basic isolation to achieve system redundancy. It can ensure system security when single-stage isolation fails. In this way, the isolation voltage can reach 5kV and above.
4. Reinforced isolation is also single-stage isolation, but it can achieve the same isolation strength as dual isolation.

Classification and Definition of Isolation Levels
Standards and Specifications for Isolator Certification
Currently, most common isolators adopt basic and reinforced isolation. In order to be certified for the two isolation levels, the performance of isolators needs to comply with regional codes and safety standards.
In terms of isolator standards and certifications, the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) is the earliest non-governmental international electrotechnical standardization organization in the world. IEC works with organizations in multiple regions to develop international safety standards for electrical/electronic devices. In different regions, local standards are developed by different organizations. For example, the United States, Canada, Germany, and China all have local organizations.
Isolators must meet local standards before they can be legally marketed commercially and the electrical/electronic products fitted with them can be sold to customers. Typically, the first page of an isolator datasheet will list standards that the isolator has passed. The reinforced isolation level of Digital Isolators is mainly proposed by VDE and promoted by IEC as a global standard. NOVOSENSE is a leader of digital isolators in China and also the first semiconductor company to obtain the VDE enhanced isolation certification.

Standards and Certification Organizations for Isolators
Under the current VDE standards, both basic and reinforced isolators have corresponding test standards and parameter specifications.
In the maximum surge voltage test, both basic and reinforced isolators are required to pass 50 bipolar surge impulses, and the final measured voltage must not exceed 1.3 times the maximum surge voltage in the datasheet, on top of which reinforced isolators are required to pass a surge voltage test of at least 10kV.
In applications, partial discharge phenomenon occurs when there are defects inside a device. which does not affect the insulation strength in short time. However, under the repeated impact of high voltage, the defect will eventually lead to the breakdown of the isolation barrier. Therefore, these defects need to be detected through non-destructive testing. Basic isolators need to pass the 1.5 times VIOSM surge test, while partial discharge testing of reinforced isolators needs to be conducted at 1.875 times VIOSM voltage.
According to the working life of chips at different temperatures and voltages, the working voltage of chips under the minimum rated life and failure rate during the target life can be fitted by Weibull distribution, and then VIORM and VIOSM can be obtained according to the requirements of the VDE correlation coefficients. It can also be seen from the table that reinforced isolators have a longer working life and a lower failure rate during their life.
After passing the above tests, isolators are deemed to have met the requirements for VDE certification.
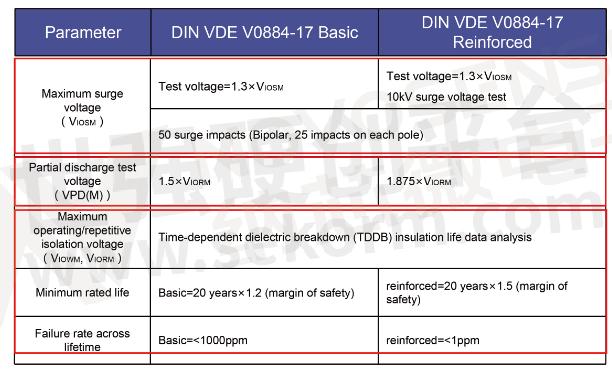
Standards and Certification for Basic and Reinforced Isolators
To sum up, electrical isolation involves the working safety of devices and the personal safety of users, and is an indispensable part of electrical system design.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.


























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































