Are All UPS Systems the Same?

UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) systems play a vital role in safeguarding electronic equipment from power disruptions, ensuring continuous operation and protecting against data loss. However, not all UPS systems are created equal. The choice of a UPS system depends on specific factors, including the application requirements, the criticality of the load, and the environmental conditions. In this article, we explore three common types of UPS systems, their applications, and essential considerations for choosing the right UPS for your needs.
Three Common UPS systems types
There are different types of UPS systems, each offering varying levels of protection and efficiency. The three main types are:
◆Standby UPS
Standby UPS is also called offline system. In this system, normally AC input (utility power) is output as is to connected devices and when a power outage or abnormal voltage is detected, inverter starts feeding using power from the batteries. In the event of a power outage, a few milliseconds of momentary break occurs in AC output.
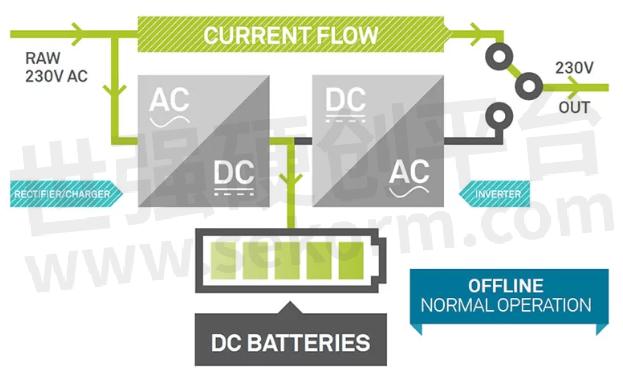
Fig.1
◆Line-Interactive UPS
Compared to Standby UPS, line-interactive UPS adds an additional feature that corrects minor fluctuations in voltage without switching to battery power. AC power passes through a voltage regulator, which corrects low and high voltages as needed, and switches to battery backup mode when a power failure is detected.

Fig.2
◆Online (Double-Conversion) UPS
An online UPS system is also called double conversion, which is a system continually converts AC power to DC and then back to AC. In a Double-conversion UPS battery backup, the input AC is charging the backup battery source which provides power to the output inverter, so the failure of the input AC won't cause activation of the transfer switch. That is to say, if a power loss occurs, the rectifier will simply drop out of the circuit and the batteries will keep the power steady and unchanged. No transfer time during the failure.This double-conversion process isolates critical loads from raw utility power completely, ensuring that IT equipment receives only clean, reliable electricity.
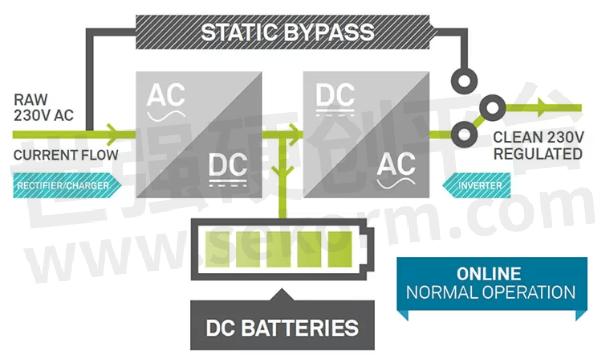
Fig.3
What's the applications of UPS system?
There's no one-size-fits-all UPS system. UPS systems differ depending on the application and usage requirements. The four central UPS systems have significant differences, including the following:
◆Consumer systems: Consumer UPS systems keep electronics and appliances running for individuals and some small businesses.
Industrial systems: An industrial UPS must support power-heavy devices, handle the required voltage, and back up critical infrastructure. Industrial systems generally require more than a UPS alone for extended power outages. The UPS serves as an intermediary, maintaining operations and backing up data until operators can connect to a secondary power source, such as a generator.
◆Medical systems: Due to the critical need for uninterrupted power, a medical-grade UPS is designed with the highest-performance electrical components on the market to meet the IEC 60601 safety standards. Lithium-ion batteries, specifically LFePO4 batteries (Lithium Iron Phosphate), are widely used in medical UPS systems due to their compact, lightweight, and long-life attributes. And, like any other lithium battery, these can be charged very fast, typically within 2 hours.
◆Data Centers and Telecommunications: UPS systems are essential in data centers to protect servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and other critical IT infrastructure from power outages and fluctuations. Telecommunication systems, including base stations, switching centers, and communication networks, rely on UPS systems to maintain continuous operation and prevent service interruptions.
◆Financial and Educational Institutions: Banks and financial institutions use UPS systems to protect computer systems, ATMs, and servers, preventing data loss and financial transaction disruptions. UPS systems are employed in schools, colleges, and universities to safeguard computer labs, servers, and educational technology infrastructure from power interruptions.
How to choose UPS systems?
The choice of UPS system depends on the specific application and the requirements of the equipment being protected. When choosing a UPS system, it's essential to consider factors such as the criticality of the equipment, the type of load, the size of the installation, and the specific power quality challenges faced in the particular application. Here are UPS systems categorized by their applications:
Home and Small Office Applications
◆Standby (Offline) UPS: Suitable for protecting personal computers, home entertainment systems, and small office equipment. Provides basic protection against power outages.
Business and Commercial Applications
◆Line-Interactive UPS: Commonly used for small to medium-sized servers, network equipment, and workstations in offices.
◆Online (Double Conversion) UPS: Ideal for critical business applications, including servers, data centers, and communication equipment.
Data Centers and IT Infrastructure
◆Online (Double Conversion) UPS: Offers the highest level of protection for data centers, server rooms, and critical IT infrastructure.
Healthcare Applications
◆Online (Double Conversion) UPS: Critical for medical equipment, ensuring a continuous power supply to diagnostic and life-support systems.
Telecommunications
◆Online (Double Conversion) UPS: Ensures continuous power for telecommunications infrastructure, including base stations, switching centers, and network equipment.
Retail and Point of Sale (POS) Systems:
◆Standby (Offline) UPS: Provides basic protection for cash registers, POS systems, and other point-of-sale equipment in retail environments.
Educational Institutions
◆Line-Interactive UPS: Used to protect computers, servers, and other electronic equipment in educational settings.
Residential Applications:
◆Standby (Offline) UPS: Protects home electronics, computers, and entertainment systems from power outages.
Transportation Systems
◆Line-Interactive UPS: Used to protect control systems, signaling equipment, and communication systems in transportation infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, not all UPS systems are the same, and the choice depends on the specific needs of the application. Whether it's a standby UPS for a home office or an online UPS for a data center, understanding the different types and their applications is crucial for effective power protection. By considering load requirements, criticality, and environmental factors, businesses can select the right UPS system to ensure uninterrupted power and protect their valuable electronic assets. As a global leader in lithium battery cell manufacturing, Grepow offers professional customization solutions for UPS battery packs and Battery Management Systems (BMS), catering to your specific application requirements.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
- Introduction to L Shaped Batteries
- Omnergy brand CR Series Button Batteries Have Low Self-discharge Characteristics and Can Be Stored for A Long Time to Reduce Power Loss
- Can Lithium Batteries and Lead Acid Batteries be Used Together?
- What are the Characteristics and Application Fields of Button Batteries?
- Lijia CR123A Lithium Manganese Cylindrical Batteries with the Single Battery Rated Voltage of 3V
- Supercapacitors vs. Batteries: A Comparison in Energy Storage Solutions
- Volume 3 Changes in Applications Using Li-ion Batteries -Customer Transition along with Application Expansion
- RRC Batteries & Power Solutions for Robotics with a Worldwide Product Certificates and Approvals
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.





























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































