How to start with SBAS mode?

Brief Introduction
A Satellite Based Augmentation System (SBAS) is a wide area differential Global Navigation Satellite System signal augmentation system that uses a number of geostationary satellites, able to cover vast areas, to broadcast primary GNSS data which has been provided with ranging, integrity, and correction information by a network of SBAS ground stations. While the primary purpose of SBAS is to provide integrity assurance, the use of the system also increases the accuracy and reduces position errors to less than 1 meter.
Compared with general GNSS positioning, SBAS is capable of covering vast areas, increasing accuracy, and reducing position errors to less than 1m. At present, the world's leading powers have also developed their own satellite navigation systems, such as the WAAS system of the United States, the EGNOSS of the European Union, the MSAS of Japan, the GAGAN of India, the SDCM of Russia, and the BDSBAS of China under development.
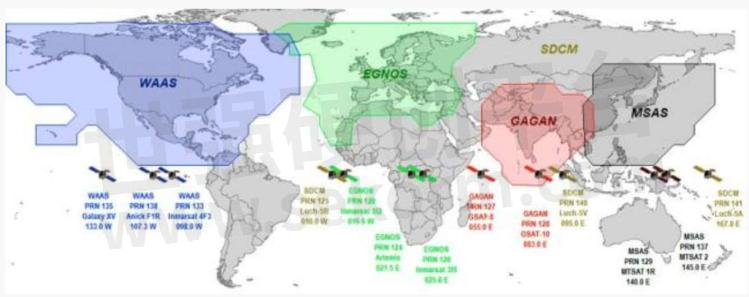
SBAS Global Distribution Map
Working Principle
The satellite-based augmentation system is composed of four parts: space constellation, ground control station, operation and maintenance station, and user. Users can broadcast a variety of correction information such as ephemeric error, satellite clock error, ionospheric delay, etc., through the geostationary orbit (GEO) satellite carrying satellite navigation augmented signal repeater to improve the positioning accuracy of the original satellite navigation system.
The navigation satellite is monitored by widely distributed differential stations (with known positions), and the original positioning data (pseudo-range, carrier phase observation values, etc.) are obtained and sent to the central processing facility (main control station). Then GNSS data from satellites are compared against the precisely documented locations of each land-based monitor. Any discrepancy is determined to be an error. Error corrections are sent to geostationary satellites and broadcast throughout the region.
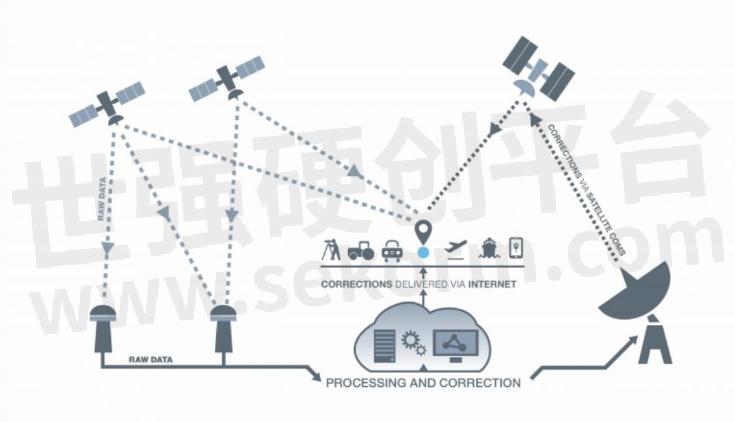
SBAS Schematic Diagram
GNSS accuracy can reach around five meters while using SBAS, users can achieve an accuracy of two meters or better. Some receivers or OEM boards can apply SBAS corrections with additional techniques to achieve sub-meter or better accuracy. Here's a step-by-step guide for you to start with SBAS mode.
We’ll take the ComNav K803 OEM module as an example. The control software is CRU, one of ComNav’s self-developed software for OEM board testing, setup, data recording, data download, and information display, you can download it for free from the ComNav website.

ComNav GNSS OEM Board
Enable SBAS Mode
The default setting for SBAS is disabled. Users can send the following commands to activate SBAS mode in CRU software:

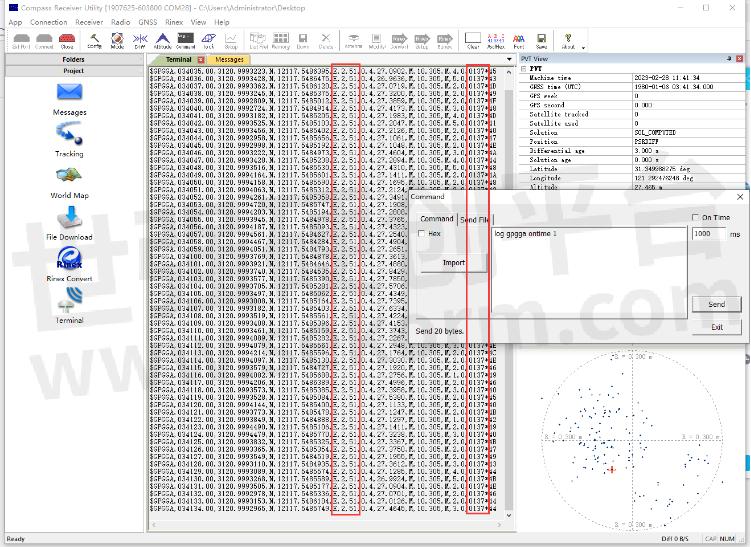
Status checking with GPGGA message
After sending the above commands, normally it will take 2-5 minutes to search SBAS satellites, then the board will go into the SBAS solution. You can request a GPGGA message with the command “log gpgga on time 1” to check the solution status. In SBAS mode, the solution status should be “2” and the base ID should be the SBAS satellite's PRN.
An example of GPGGA message: $GPGGA,015101.00,3121.0000551,N,12117.5483125,E,2,23,1.1,37.2598,M,0.000,M,02,0137*5
Troubleshot
If it takes a longer time and cannot access SBAS mode, you need to check first if the configuration is successful.
Enter “LOG SYSCONFIG” to check whether SBAS mode is enabled. Enable means SBAS enabled, and Disable means SBAS not enabled.
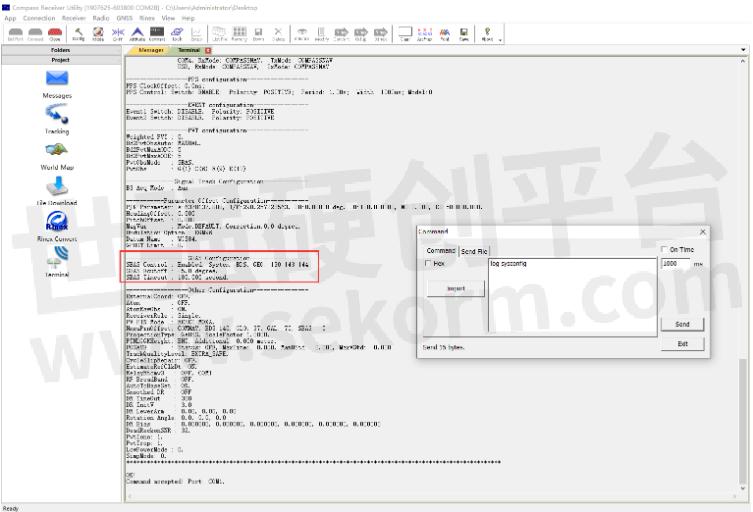
If the SBAS mode is enabled, and still cannot go into SBAS mode, you can use the command ” Log Testinfor” to check if the SBAS satellite is searchable. The satellites marked with S are SBAS satellites.
Accuracy analysis
With a brand-new SBAS engine, currently we verified in Japan-MSAS, China-BDSBAS, India-GAGAN, and Europe-EGNOS. The SBAS accuracy can be very stable at 0.6 horizonal.
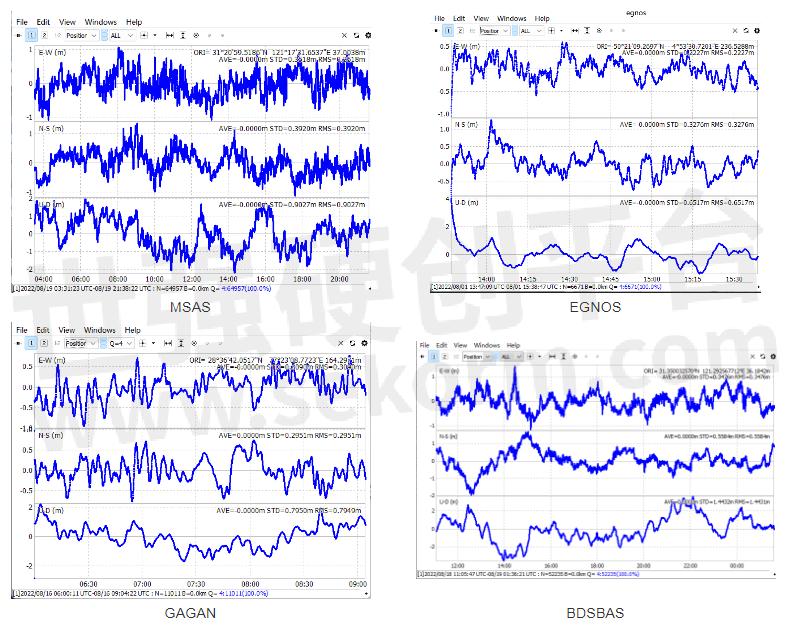
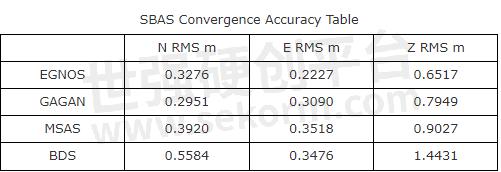
So far, the SBAS system is widely used in industries across aerospace, geodesy, marine navigation, personnel positioning, settlement monitoring, and other fields. Consequently, it performs well even in challenging situations, such as complex terrain, valleys, or areas with strict requirements for navigation. The most prominent benefit of SBAS is cost saving as it enables to location without receiving network differential.
About Comnav Technology
ComNav Technology is the major provider of GNSS OEM boards, receivers, and high-precision positioning solutions, encompassing product development, and marketing. Its technology and products have already been applied in a wide range of fields such as surveying, construction, machine control, agriculture, intelligent transportation, precise timing, deformation monitoring, and unmanned system. With its experienced team and innovational spirit, ComNav Technology is always trying its best to provide reliable and competitive products to global customers. In 2015, ComNav Technology was listed on the China National Equities Exchange and Quotations (NEEQ), Securities: ComNav Technology (Compass Navigation), Stock code: 833972.
About SinoGNSS®
SinoGNSS® is the official trademark of ComNav Technology Ltd., registered in the People’s Republic of China, EU, USA, and Canada. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
- +1 Like
- Add to Favorites
Recommend
This document is provided by Sekorm Platform for VIP exclusive service. The copyright is owned by Sekorm. Without authorization, any medias, websites or individual are not allowed to reprint. When authorizing the reprint, the link of www.sekorm.com must be indicated.
























































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































