
Industrial solid state drive (SSD) manufacturers are scrambling to extend endurance and constantly edging one another out in the bid to put out the “highest” endurance and “longest-lasting” specifications.
While it is easy to be impressed by these high numbers, it is wise to be discerning about several nuanced factors beyond specifications like terabytes written (TBW) or drive writes per day (DWPD). After all, you need these industrial SSDs to last as long as possible and to deliver reliable performance according to their rated lifespan or even beyond.
Instead of merely looking at raw endurance specifications, prospective users and buyers should also consider evaluating NAND Flash endurance from a cost-per-endurance and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) perspective.
SSDs with an initial lower purchase cost but may turn out to be more expensive in the long run due to frequent replacements and higher operational costs due to disruptions and downtime, all of which will raise the TCO. This is like buying low-quality tires that let you save upfront but eventually cause not only inconvenience but also higher costs over time. This article delves into the key factors beyond endurance specifications to guide you in your procurement decisions.
Limitations of Solely Relying on TBW and DWPD
TBW refers to the total amount of data that can be written on an SSD throughout its lifetime before the NAND flash wears out. DWPD, on the other hand, shows how many times the entire capacity of the drive can be written per day throughout its warranty period.
While TBW and DWPD help users estimate an SSD’s lifespan, their accuracy in predicting the actual lifespan may be affected by the following:
Uniform Write Patterns are typically used to arrive at these numbers; however, real-world usage varies in several ways that these metrics may not capture.
Environmental and Operational Conditions. Flash wear is not just brought about by total bytes written. It is influenced by temperature, power cycling, write amplification, internal management functions like garbage collection and wear leveling, and other factors.
Warranty Assurance. These metrics typically represent the guaranteed minimum endurance in accordance with warranty requirements. SSDs may function beyond these numbers, but the manufacturer will no longer provide the assurance of reliability.
Workload Type: Sequential vs. Random
Before deciding on which SSD to purchase, check if the endurance specs are based on realistic workload patterns matching the application use and expected workload type. There are generally two workload types:
Sequential. These are reads/writes in large continuous blocks. They are considered less taxing to the SSD, which means that sequential reads/writes do not wear out the NAND flash as much or as fast.
Random. These are reads/writes in small, scattered blocks. They cause more write amplification, which reduces endurance.
Beyond raw sequential or random ratings, reliable SSD endurance specs should reflect and mimic realistic workloads and application behaviors including write amplification factors (WAF) caused by garbage collection, as well as parameters such as temperature, active use time, data retention, and error rates.
To give a comprehensive understanding of SSD endurance, ATP provides both sequential and random TBW (Total Bytes Written) ratings. This dual approach helps users evaluate drive endurance under different real-world usage scenarios.
ATP’s TBW ratings may vary depending on application, and endurance can be predicted based on several factors such as:
Usage conditions applied to the device
Internal NAND component cycles
Write amplification factor (WAF)
Wear leveling efficiency of the drive
The following table shows test methodologies and typical applications recommended for respective endurance ratings:
| Endurance Rating | Test Methodology | Typical Application |
|---|---|---|
| Sequential TBW | 128K block size, pure sequential writes | Streaming, large file transfers |
| Random TBW | JESD219A enterprise workload | Databases, mixed/random access |
NAND Flash Configuration Tradeoffs: TLC or pSLC
NAND technology has evolved by increasing the number of bits stored per cell. From single-level cell (SLC) storing 1 bit per cell, multi-level cell (MLC) storing 2 bits, triple-level cell (TLC) storing 3 bits, to quad-level cell (QLC) storing 4 bits per cell.
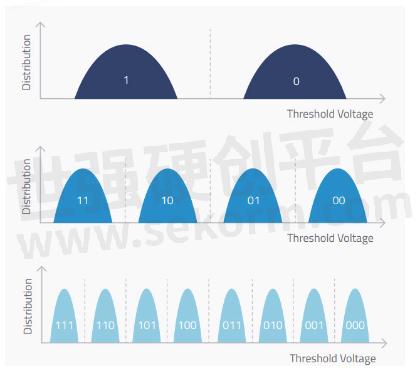
To mimic SLC’s characteristics, pseudo SLC (pSLC) mode is achieved by configuring TLC to operate as SLC, storing only 1 bit per cell instead of 3, hence when TLC NAND flash is converted to pSLC mode, the storage capacity is reduced to one third of its original value, but general endurance is increased to more than 10X of the same TLC products. For applications requiring higher endurance and performance, and can trade off some capacity, such as write-intensive industrial or enterprise applications, look for drives supporting pSLC mode.
ATP Electronics offers a wide range of SSDs with different NAND flash configurations. ATP pSLC drives are purpose-built to extend the general endurance to more than 10X of the same TLC products. Writing only 1 bit per cell, these drives deliver faster write speeds, lower latency, enhanced reliability, and power efficiency, all for a fraction of the cost of true SLC.
Overprovisioning: More Spare Blocks = Higher Endurance
Overprovisioned (OP) space refers to the practice of reserving a certain portion of the SSD for controller management functions. The spare blocks are not accessible to the user. They help ensure that NAND maintenance tasks, such as wear leveling, garbage collection, bad blocks management, and error correction run in the background more efficiently.
The lower OP percentage offers more capacity for users but leads to faster SSD degradation and more frequent drive replacements. High OP settings reduce WAF and distribute wear more evenly. Users who are willing to trade off capacity for extra performance and endurance should opt for SSDs with higher OP.
ATP SSDs typically allocate 7% over-provisioning (OP) space by default. This default setting balances user capacity with reliable performance and endurance. However, ATP can customize OP percentages for specific projects or products.
| OP Percentage | User Capacity | Write Amplification Factor (WAF) | Wear Distribution | Endurance | Typical Use Case/Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low OP | Higher (more user space) | Higher (more frequent internal writes) | Less even (localized wear) | Lower endurance | Users prioritizing capacity |
| High OP | Lower (less user space) | Lower (fewer internal writes) | More even (better wear leveling) | Higher endurance | Users willing to trade capacity for improved endurance |
Don’t Overlook Data Retention
While many manufacturers flaunt high endurance numbers, data retention, which shows how long data is preserved without power, is also very important, as poor retention makes endurance numbers insignificant if data is corrupted or lost after the SSD is powered off.
Data retention for SSDs describes how long the drive can reliably store data without power before the drive can no longer read the data. This period is influenced by several factors, primarily the percentage of program/erase (P/E) cycles used and the storage temperature.
Lower P/E Usage = Longer Retention. Drives that have used a smaller portion of their P/E cycles (e.g., 10%) retain data much longer than those near end-of-life.
Higher Storage Temperatures Reduce Retention Time. Higher storage temperatures, such as 55°C, significantly reduce data retention, as elevated heat accelerates charge loss. At lower temperatures (like room temperature), retention is typically longer.
The Arrhenius equation (used in SSD reliability engineering) is generally useful in estimating NAND flash retention times. According to this, retention time increases exponentially as temperature decreases. For example, going from 55°C down to 40°C potentially extends retention by a factor of 5–6 times.
While the Arrhenius equation mathematically expresses how lower temperatures should significantly extend data retention, NAND flash is inherently complicated and degradation can be attributed to several factors such as charge loss, trap generation, and oxide stress. Advanced charge-trap technologies introduce multiple complex data loss mechanisms that do not always follow expected temperature trends, making traditional predictions less reliable for today’s SSDs. ATP’s whitepaper, “Limitations of Arrhenius Law in Data Retention Time Estimation,” highlights these issues, cautioning against relying solely on the Arrhenius model.
In addition, “How to Estimate NAND Flash Retention Times Under Specified Mission Temperature Profiles,” offers practical methods for more accurate retention estimates. It recommends using real-world temperature exposure data and a tabular approach to account for the full range of conditions a device experiences—especially important in industrial and automotive applications. For a thorough understanding of flash data retention in demanding environments, both documents are highly recommended.
ATP typically specifies data retention at 100% P/E cycles (fully worn NAND) and 55°C storage temperature for these reasons:
Industry Standard. Organizations like JEDEC define SSD data retention requirements at end-of-life wear (100% P/E) and elevated temperature (often 55°C). This creates a consistent, comparable baseline across vendors and products.
Worst-Case Scenario. 100% P/E at 55°C represents the harshest, most demanding conditions a drive might face. If the SSD can retain data for a guaranteed period under these conditions, it is even more reliable under lighter use or cooler storage.
Why ATP is Confident in Leading Industrial SSD Endurance
ATP’s confidence in claiming the highest endurance for industrial SSDs is rooted in a rigorous, transparent approach to both product design and validation.
ATP’s Specialized Capabilities. The use of prime NAND package, strict NAND IC characterization, 100% NAND screening and validation capabilities, as well as ATP’s proprietary firmware, specialized hardware configurations, and own-developed technologies are just some of the specialized capabilities that boost and enhance the inherent qualities of the NAND flash.
ATP’s Comprehensive Testing Approach. This entails a thorough assessment of the NAND flash’s overall endurance under different test methods to evaluate performance across various aspects, such as:
Initial read/write operations
Endurance (P/E cycles)
Data retention
Cross-temperature behavior
Read disturb characteristics
Error correct reliability, erase/program/read (EPR), and other endurance tests ensure robust performance and endurance characteristics under a range of environmental and operational conditions.
Conclusion: Endurance in the Real Sense
As the endurance wars rage on, it is important to look beyond what the specifications say. TBW and DPWD are key metrics, but behind these metrics, buyers should also look at workloads, NAND configurations, overprovisioning, and data retention.
Buyers are also recommended to look at SSD’s endurance from a cost-per-endurance / total cost of ownership value proposition. By considering not only the initial purchase price but also reflecting on the comprehensive cost throughout the SSD’s lifespan, buyers will have a more realistic picture of the true cost and long-term value of the storage device.
For inquiries about ATP’s endurance specifications and its wide range of high-endurance memory and storage solutions, please visit the ATP website or contact an ATP representative in your area.










































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































